Treatment for cancer of the vagina can be done with surgery, laser, chemotherapy, radiation therapy or topical therapy, depending on the type and size of the cancer, staging of the disease and general health of the patient.
The symptoms of cancer can be runny nose, pain during intimate contact and pain when urinating. Cancer in the vagina is rare and usually affects women between the ages of 45 and 64.
The chance of cure for cancer of the vagina reduces the later the treatment starts, but according to statistics, half of the patients with cancer of the vagina can heal.
Radiation therapy for vaginal cancer
Radiation therapy for cancer in the vagina uses radiations to destroy, or reduce the growth of cancer cells and can be done in conjunction with low doses of chemotherapy.
Radiation therapy can be applied by external radiation through a machine that emits radiation beams on the vagina and should be performed 5 times a week for a few weeks or months. If it is brachytherapy, the radioactive material is placed close to the cancer and can be given at home 3 to 4 times a week, at 1 to 2 weeks apart.
The side effects of radiation therapy for cancer in the vagina can be:
- Tiredness;
- Diarrhea;
- Nausea;
- Vomiting;
- Weakening of the bones of the basin;
- Vaginal dryness;
- Narrowing of the vagina.
Usually the side effects disappear after a few weeks after the treatment is finished. If radiation therapy is given in conjunction with chemotherapy, the adverse reactions to treatment are more intense.

Chemotherapy for vaginal cancer
Chemotherapy for cancer in the vagina uses oral or directly into the vein remedies, which may be cisplatin, fluorouracil, or docetaxel, which will destroy the cancer cells located in the vagina or scattered throughout the body. It can be performed before surgery to reduce the size of the tumor and is the main treatment used to treat highly developed vaginal cancers.
Chemotherapy does not only attack cancer cells but also normal cells in the body, so there may be side effects of chemotherapy for vaginal cancer such as:
- Hair loss;
- Wounds in the mouth;
- Lack of appetite;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Diarrhea;
- Infections;
- Changes in the menstrual cycle;
- Infertility.
The severity of the side effects depends on the medicine used and the dosage, and usually disappear after a few days after treatment.
Surgery for vaginal cancer
The surgery for cancer in the vagina aims to remove the tumor located in the vagina so that it does not increase in size, or does not spread through the rest of the body.
There are several surgical procedures that can be performed such as:
- Local excision, which consists of removal of the tumor and a part of the healthy tissue of the vagina;
- Vaginectomy, which consists of total withdrawal or part of the vagina and is indicated for tumors of large size.
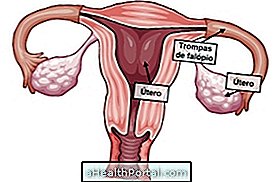
Sometimes the removal of the uterus may be necessary to prevent the onset of cancer in this organ. The lymph nodes in the basin region should also be removed to avoid spreading cancer cells.
The recovery time of the surgery varies from woman to woman, but it is important to rest and avoid having intimate contact during the healing time. In cases where the vagina is completely withdrawn, it can be reconstructed with excerpts of skin or another part of the body, which will allow the woman to have intercourse.
Generally, surgery followed by radiation therapy is sufficient to cure the disease.
Laser surgery for vaginal cancer
Laser surgery for cancer of the vagina involves the application of a high-energy beam of light on the site where the cancer cells are in the vagina. Generally, this treatment is effective in large lesions, however, it has no results in invasive cancer, that is, when it can spread to other organs.
Topical therapy for vaginal cancer
Topical therapy for cancer of the vagina consists of the application of creams or gels directly on the tumor located in the vagina, in order to prevent the growth of cancer and eliminate the cancerous cells.
One of the medicines used in topical therapy is Fluorouracil, which can be applied directly to the vagina once a week for about 10 weeks or at night for 1 to 2 weeks. Imiquimode is another medicine that can be used.
The side effects of topical therapy for cancer in the vagina can be severe irritation of the vagina and vulva, dryness and redness. Although it is in some effective cancers, this treatment does not have as good a result compared to surgery.