Breath is a sound of turbulence suffered by the blood during the passage through the heart, passing through its leaflets or clashing with your muscles. Not every breath indicates heart disease, as it happens in many healthy people, and in these cases it is called a physiological or functional breath.
However, the murmur may also indicate a defect in the heart valves, heart muscles or a disease that changes the speed of blood flow, such as rheumatic fever, anemia, mitral valve prolapse or congenital diseases, for example.
In some cases these situations can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, swelling in the body and palpitations and, in these situations, the treatment should be performed as soon as possible, with the use of medicines or undergoing surgery, under the guidance of the cardiologist.

Main symptoms
Generally, the heart murmur is not accompanied by other signs or symptoms, and its presence alone is not serious. However, when the murmur is caused by a disease that causes difficulties in the functioning of the heart, symptoms may appear that indicate difficulties in pumping blood and oxygenating the body cells.
Some of the main symptoms are:
- Shortness of breath;
- Cough;
- Palpitations;
- Weakness.
In babies, it is common to notice the difficulty in breastfeeding, weakness and presence of mouth and purplish hands, and this is due to the difficulty in oxygenation of the blood, since the heart does not function correctly.
What causes heart murmur
The murmur in the heart is a sign, which may be physiological, but may also indicate some type of change or disease, for various causes, both in adults and children.

Heart murmur for children
In infants and children, the main cause of bloating is benign and disappears over time, usually due to lack of development of heart structures, which may be disproportionate.
However, it can also be due to the presence of a congenital disease in the formation of the heart, which is already born with the child due to genetic diseases or intercurrences during pregnancy, such as rubella infection, use of some drugs, alcoholism or drug use of the pregnant woman. There are several types, but the most common defects that can cause blowing are:
- Defects in cardiac chambers or valves, such as mitral valve prolapse, bicuspid aortic valve, aortic stenosis, or coarctation of the aorta, for example;
- Communication between the chambers of the heart, which may occur due to a delay or defect in closure in the muscles of the cardiac chambers, and examples are the ductus arteriosus, interatrial or interventricular communications, atrioventricular septal defects, and tetralogy of Fallot.
The milder conditions may be accompanied by the pediatric cardiologist, or improved with the use of medicines, such as the anti-inflammatory drugs used in the patent ductus arteriosus. However, when the change is severe enough to cause symptoms such as mouth and purple limbs, it is important to schedule a surgery.
Learn more about identifying a congenital heart disease.
Heart murmur in adult
The heart murmur in adults also does not indicate the presence of disease, and in many cases, it is possible to live with it normally, and even to practice physical exercises, after release by the cardiologist. However, the presence of this signal may also indicate the existence of a change, such as:
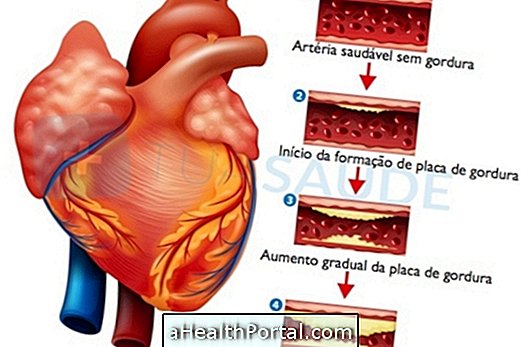
- Narrowing of one or more heart valves, called stenosis, due to diseases such as rheumatic fever, age calcification, tumor or inflammation by a heart infection, for example, that prevent the free passage of blood during heartbeat;
- Insufficiency of one or more valves due to diseases such as mitral valve prolapse, rheumatic fever, dilatation or hypertrophy of the heart or some type of alteration that prevents the correct closure of the valves during the pumping of the heart;
- Diseases that alter the blood flow, such as anemia or hyperthyroidism, that cause blood swirling during its passage.
The diagnosis of heart murmur can be made by the general practitioner or cardiologist during the clinical exam of auscultation of the heart, and its confirmation is made by imaging tests, such as the echocardiogram.
How to treat
In most cases, the treatment of the physiologic heart murmur is not necessary, with a follow-up every 6 or 12 months with the cardiologist. However, if there are symptoms or clinical manifestations of any disease, the heart needs to be treated with medicine or surgery.

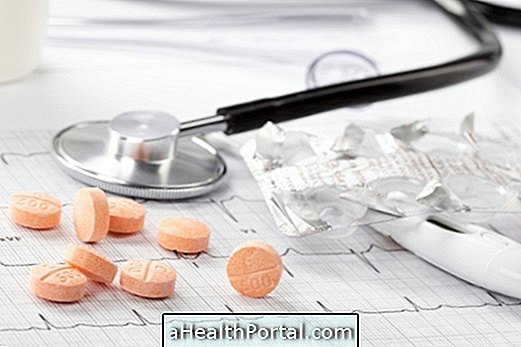
Treatment with medicines
The treatment involves drugs to control the pressure and to facilitate the work of the heart, with medicines that control its frequency like propranolol, metoprolol, verapamil or digoxina, that diminish the accumulation of liquids in the lungs, like diuretics, and that control the pressure and facilitate the passage of blood through the vessels, such as hydralazine and enalapril.
Treatment with surgery
The surgery is indicated by the cardiologist and cardiac surgeon, after evaluation of factors such as symptoms that do not improve with medication, severity of the defect in the heart and presence of other signs such as heart failure or arrhythmia.
The surgery options are:
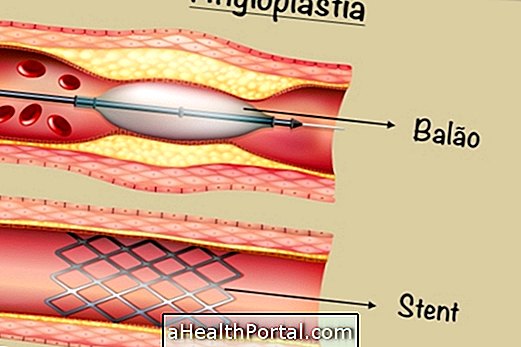
- Correction of the valve by balloon, made with the introduction of a catheter and insufflation of a balloon, being better indicated for cases of narrowing;
- Correction by surgery, done with the opening of the thorax and the heart to correct the defect in the valve or in the muscle;
- Valve exchange surgery, which can be replaced by a synthetic or metal valve.
The type of surgery also varies according to each case and with the indication of the cardiologist and cardiac surgeon.
Initial recovery from cardiac surgery is usually done in the ICU for about 1 to 2 days. Then the person will remain in the hospital, where he will undergo cardiologist evaluations until he can go home, where he will stay for a few weeks without effort and recovering.
In the recovery period, it is important to take care of a healthy diet and practice physical therapy. Learn more details on how the postoperative period of heart surgery is.
Heart murmur in pregnancy
In women who have some type of silent heart defect or mild heart murmur, pregnancy can cause clinical decompensation, causing symptoms such as severe shortness of breath and palpitations. This is because, in this period, there is an increase in blood volume and the amount of blood pumped by the heart, which requires more work by the organ. Learn more about the possible causes of shortness of breath in pregnancy.
In these cases, medication can be given to control the symptoms, and if there is no improvement and surgery is needed, it is preferably done after the second trimester, when the pregnancy is more stable.