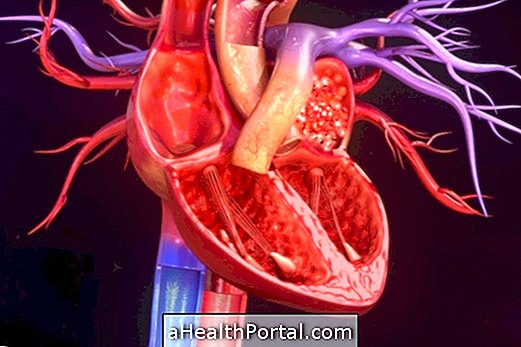
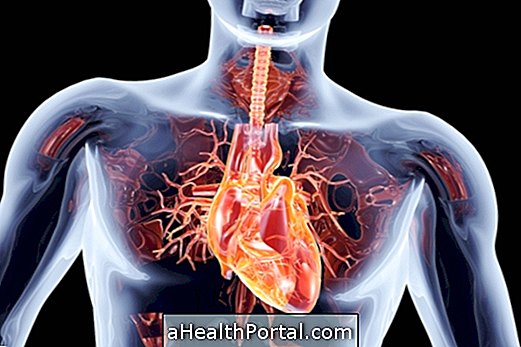
Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI), also known as infarction or heart attack, is a disruption of blood flow to the heart, which causes the death of heart cells and causes symptoms such as chest pain that can radiate to the arm.
The main cause of the infarction is the accumulation of fat inside the vessels, often resulting from unhealthy habits, a diet rich in fat and cholesterol and poor in fruits and vegetables, as well as sedentary lifestyle and genetic factors.
The diagnosis is made by the cardiologist through physical, clinical and laboratory tests and the treatment is done with the purpose of unclogging the artery and improving blood circulation.

Causes of AMI
The main cause of acute myocardial infarction is atherosclerosis, which corresponds to the accumulation of fat inside the blood vessels, in plaque forms, which can hinder the passage of blood to the heart and thus cause a heart attack. In addition to atherosclerosis, acute myocardial infarction may occur due to non-atherosclerotic coronary disease, congenital abnormalities and hematological changes, for example. Learn more about what can cause the heart attack.
Some factors can increase the chances of the infarction, such as:
- Obesity, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, diet rich in fat and cholesterol and poor in fiber, fruits and vegetables, these factors are called risk factors modifiable by lifestyle;
- Age, race, gender and genetic conditions, which are considered non-modifiable risk factors;
- Dyslipidemia and hypertension, which are factors modifiable by drugs, that is, that can be solved through the use of medications.
To prevent heart attack, it is important that the person has healthy lifestyle habits, such as exercising and eating properly. See what to eat to lower cholesterol.
Main symptoms
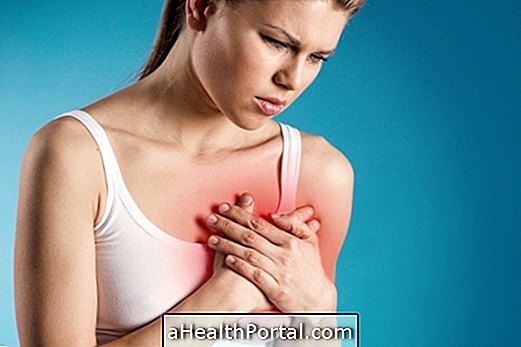
The most characteristic symptom of acute myocardial infarction is pain in the form of a tightening of the heart, on the left side of the chest, which may or may not be associated with other symptoms, such as:
- Dizziness;
- Malaise;
- Nipple;
- Cold sweat;
- Pallor;
- Feeling of weight or burning in the stomach;
- Throat tightness;
- Pain in the armpit or left arm.
As soon as the first symptoms appear it is important to call SAMU because the infarction may result in loss of consciousness, since there is a decrease in the blood supply to the brain. Learn how to identify the heart attack.
If you see an infarct with loss of consciousness, ideally you can do a heart massage while waiting for the arrival of SAMU, as this increases the chances of survival of the person. Learn how to do a heart massage in this video:

Diagnosis of Acute Myocardial Infarction
The diagnosis of AMI is made through physical exams, in which the cardiologist analyzes all the symptoms described by the patient, in addition to the electrocardiogram, which is one of the main diagnostic criteria for the infarction. The electrocardiogram, also known as ECG, is an examination that aims to evaluate the electrical activity of the heart, and it is possible to verify the rhythm and frequency of heart beats. Understand what the ECG is and how it is done.
To diagnose myocardial infarction, the physician may also request laboratory tests to detect the presence of biochemical markers that have their increased concentration in infarct situations. The commonly requested markers are:
- CK-MB, which is a protein found in cardiac muscle and whose concentration in the blood increases 4 to 8 hours after infarction and returns to normal after 48 to 72 hours;
- Myoglobin, which is also present in the heart, but has its concentration increased 1 hour after infarction and returns to normal levels after 24 hours - Learn more about myoglobin examination;
- Troponin, which is the most specific myocardial infarction marker, increasing 4 to 8 hours after infarction and returning to normal levels after about 10 days - Understand what the troponin test is for.
Through the results of the cardiac marker tests, the cardiologist can identify when the infarction occurred from the concentration of markers in the blood.
How is the treatment done?
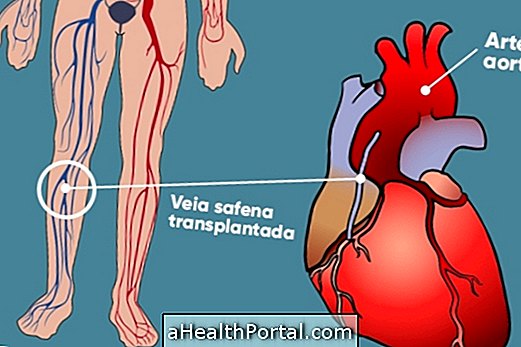
The initial treatment for acute myocardial infarction is to unclog the vessel through angioplasty or through the surgery of making bridges with vessels, such as saphenous veins taken from the leg or as the mammary arteries.
In addition, the patient needs to take medications that decrease plaque formation or make blood thinner in order to facilitate passage through the vessel, such as Acetyl Salicylic Acid (ASA), for example. Read more about infarction treatment .