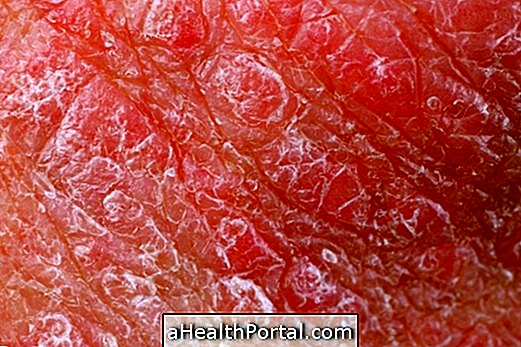
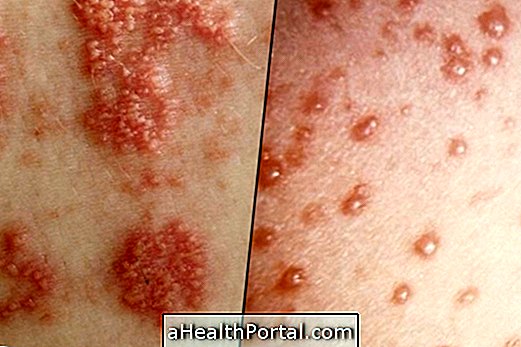
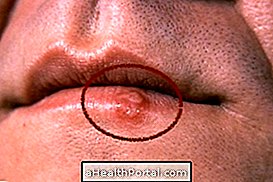
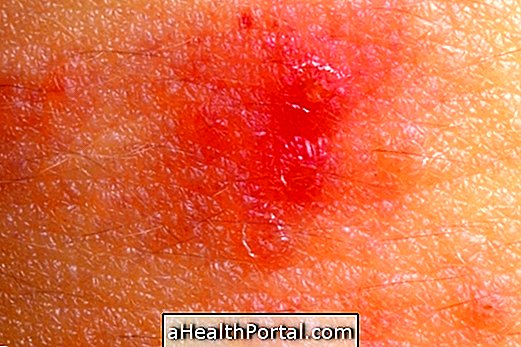
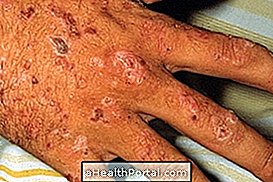
Impetigo is a skin infection caused by bacteria that lead to small sores that contain pus and a hard shell, which may be golden or honey-colored.
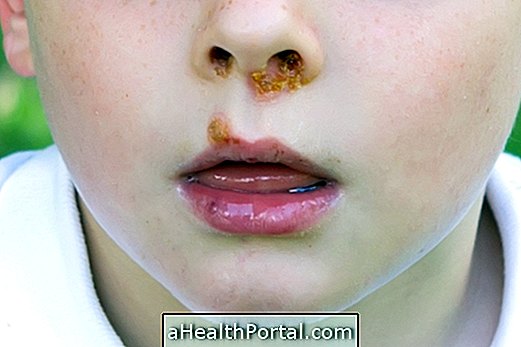
The most common type of impetigo is non-bullous, and in this case, sores always appear inside the nose and lip, however, other types of impetigo manifest in the arms or legs and feet. Popularly impetigo is also called impinge.
Symptoms and diagnosis of impetigo
To confirm if the skin lesions are impetigo, it is important to consult a dermatologist because the lesions are very contagious and caused by the excessive development of bacteria that can infect and damage several layers of the skin.
There are different types of impetigo that have slightly different characteristics and symptoms, such as:
1. Common or non-bullous impetigo
- Wounds similar to mosquito bites;
- Small skin lesions with pus;
- Wounds that progress to crusts with golden coloration or honey color
This is the most common type of disease, and it usually takes about 1 week for all symptoms to appear, especially in the regions around the nose and mouth.
2. Bullous Impetigo
- Small red sting-like wounds;
- Injuries that rapidly progress to blisters with yellowish fluid;
- Itching and redness in the skin around the blisters;
- Emergence of yellow crusts;
- Fever above 38 ° C. general malaise and lack of appetite.
Bullous impetigo is the second most common type and develops in the arms, legs, chest and belly, being rare in the face.
3. Ectima
- Open wounds with pus;
- Emergence of large yellowish crusts;
- Redness around crusts.
This is the most serious type of impetigo because it affects the deeper layers of the skin, especially in the legs and feet. This way, the treatment is more time consuming and can leave small scars on the skin.

How is the treatment done?
Treatment for this disease should be guided by a pediatrician in the case of infants and children or by a dermatologist in the case of adults, but is usually done with the application of antibiotic ointments on the lesion.
In some cases, it may be necessary to soften the crusts with warm water before applying the ointment to improve the effects of the treatment. Find out which medicines are most used and what you should do to ensure proper impetigo treatment.
In cases where the treatment has no effect, the doctor may also request laboratory tests to identify the type of bacteria that is causing the disease and to adapt the antibiotic used.
Causes and Transmission of Impetigo
Impetigo is caused by the bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes or Staphylococcus aureus that affect the most superficial layers of the skin, and anyone can develop the disease, however healthy it may be. These bacteria normally inhabit the skin, but an insect bite, cut or scratch can cause them to reach the inner layers causing infection.
This skin disease is very contagious because the bacteria are easily transmitted through contact with the pus released by the lesions. Thus, it is advised that the child or the adult stay home until 2 days after starting treatment to avoid infecting other people.
In addition, during treatment it is very important to have some care such as:
- Do not share sheets, towels, or other objects that are in contact with the affected area;
- Keep wounds covered by a clean gauze or clothing;
- Avoid touching or biting wounds, lesions or scabs;
- Wash hands often, especially before coming in contact with other people;
In addition, in the case of infants and children it is very important to let them play with washable toys only, as they should be washed 48 hours after starting treatment to prevent the infection from recurring due to bacteria that remain on the surface of the toys.