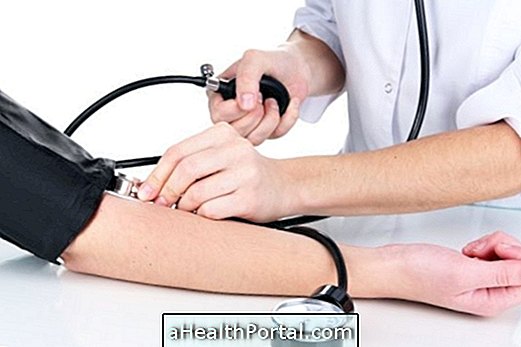
The pregnancy of the obese woman has to be more controlled because being overweight increases the risk of developing complications in pregnancy, such as hypertension and diabetes in the mother, and also problems of malformations in the baby, such as heart defects.
Although during pregnancy it is not advisable to make weight loss diets, it is essential to control the quality of the food and the intake of calories so that the baby has all the nutrients necessary for its development, without the pregnant woman to increase the weight very much.
If the woman is well above her ideal weight, it is important that she lose weight before becoming pregnant to achieve an acceptable body mass index and thus reduce the risks associated with being overweight during pregnancy. Nutritional monitoring before and during pregnancy, in such cases, is indispensable. Losing weight before getting pregnant will also help the woman feel the baby when she is pregnant because excess fat makes it hard for the overweight woman to feel her baby stirring.
How many pounds does the overweight pregnant woman gain weight during pregnancy?
The weight that a woman should gain weight during pregnancy depends on the weight of the woman before becoming pregnant, which is assessed by the body mass index, which relates the weight to the height. Thus, if the body mass index before pregnancy was:
- Less than 19.8 (underweight) - weight gain during pregnancy should be between 13 and 18 pounds.
- Between 19.8 and 26.0 (appropriate weight) - the weight gain during pregnancy should be between 12 to 16 pounds.
- Greater than 26.0 (overweight) - the weight gain during pregnancy should be between 6 and 11 pounds.
In some cases, obese women may not gain weight or gain very little weight during pregnancy because as the baby grows and the pregnancy progresses, the mother can lose weight by eating healthier and, as the weight gained by the baby compensates the mother loses, the weight on the balance does not change.
Attention: This calculator is not suitable for multiple pregnancies.

Pregnancy risks in obese woman
The risks of pregnancy in obese women involve problems for the health of the baby and the mother.
The obese pregnant woman has a higher risk of developing high blood pressure, eclampsia and gestational diabetes, but the baby may also suffer from excess weight from the mother. Abortion and the development of malformations in the baby, such as a heart defect or spina bifida, are more common in obese women, as well as an increased risk of having a premature baby.
The postpartum of the obese woman is also more complicated, with a greater risk of scarring, so slimming before pregnancy can be a great way to have a pregnancy free of complications.
Food for the obese pregnant
The nutrition of the obese pregnant woman must be balanced and varied, but the quantities must be calculated by the nutritionist so that the pregnant woman has all the nutrients necessary for the development of the baby. In addition, it may be necessary to prescribe supplements according to the body weight of the pregnant woman.
It is essential not to eat fatty foods, such as fried or sausage, sweets and soft drinks.
To learn more about what to eat during pregnancy see: Feeding in pregnancy.














-e-como-tratar.jpg)