The lack of vitamin D is very common but initially has no characteristic symptoms. There is usually only a suspected lack of vitamin D when this deficiency is too great after a prolonged lack of vitamin D, which is when signs and symptoms such as:
- Growth retardation in children;
- Bowing of the legs in the child;
- Enlargement of the extremities of the bones of the leg and arms;
- Delayed birth of baby's teeth and cavities early on;
- Osteomalacia or osteoporosis in adults;
- Weakness in the bones, which makes them easier to break, especially the bones of the spine, hips and legs;
- Pain in the muscles;
- Feeling of fatigue, weakness and malaise;
- Pain in the bones;
- Muscle spasms.
The conditions favoring vitamin D deficiency are the lack of adequate and healthy sun exposure, increased pigmentation of the skin, age over 50 years, low intake of vitamin D rich foods and living in cold places where the skin is rarely is exposed to the sun.
Light-skinned people need about 20 minutes of sun exposure per day, while darker-skinned people need at least 1 hour of direct sun exposure without sunscreen in the early morning or late afternoon.
How to confirm lack of vitamin D
The doctor may suspect that the person may have vitamin D deficiency when he or she does not adequately expose himself to the sun, always uses sunscreen, and does not consume foods rich in vitamin D. In the elderly vitamin deficiency may be suspected D in case of osteopenia or osteoporosis.
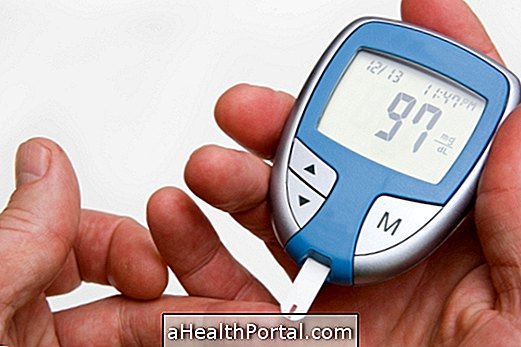
The diagnosis is made through a blood test called 25-hydroxyvitamin D, and the reference values are:
- Severe deficiency: less than 20 ng / ml;
- Mild deficiency: between 21 and 29 ng / ml;
- Appropriate value: from 30 ng / ml.
This test can be ordered by the general practitioner or pediatrician, who can assess if there is a need to take some vitamin D. Supplement Learn how the vitamin D test is done.
When to take vitamin D supplement
The doctor may recommend taking vitamin D2 and D3 when the person lives in a place where there is little sun exposure and where foods rich in vitamin D are not very accessible to the general population. In addition, it may be recommended to supplement pregnant and newborn infants up to 1 year of age, and always in case of confirmation of vitamin D deficiency.
Supplementation in case of need should be done for 1 or 2 months, and after that period the doctor may request a new blood test to assess whether it is necessary to continue taking the supplement for a longer time because it is dangerous to take excessive vitamin D, which can greatly increase the levels of calcium in the blood, which also favors bone breakage.
Main causes of vitamin D deficiency
In addition to the low consumption of foods containing vitamin D, the lack of adequate sun exposure, due to excessive use of sunscreen, brown skin, mulatto or black skin, lack of vitamin D may be related to some situations, such as:
- Chronic renal insufficiency;
- Lupus;
- Celiac disease;
- Crohn's disease;
- Short bowel syndrome;
- Cystic fibrosis;
- Cardiac insufficiency;
- Gall stones.
Thus, in the presence of these diseases, medical monitoring should be done to check vitamin D levels in the body through a specific blood test and, if necessary, take vitamin D supplements.
Important sources of vitamin D
Vitamin D can be obtained from food, by consuming foods like salmon, oysters, egg and sardines, or through the internal production of the body, which depends on the sun's rays in the skin to be activated.
People with vitamin D deficiency are more likely to develop diseases such as diabetes and obesity, so they should increase their exposure time or take vitamin D supplements according to medical advice.
Check out more examples of foods rich in vitamin D
Consequences of lack of vitamin D
Lack of vitamin D increases the chances of having serious diseases that affect bones such as rickets and osteoporosis but may also increase the risk of developing other diseases such as:
- Diabetes;
- Obesity;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Rheumatoid arthritis and
- Multiple sclerosis.


Sun exposure is important to prevent vitamin D deficiencies because only about 20% of the vitamin's daily needs are attained by diet. Adults and children with fair skin need about 20 minutes of sun exposure daily to produce this vitamin, while black people need about 1 hour of sun exposure. Learn more details on How to Safely Take Sunshine to Produce Vitamin D.