Transplantation of the uterus may be an option for women who wish to become pregnant but who do not have a uterus or who do not have a healthy uterus, making pregnancy impossible.
However, uterine transplantation is a complex procedure that can be performed only in women and is still undergoing testing in countries such as the United States and Sweden.
How is the uterus transplant done?
In this surgery, doctors remove the diseased uterus, keeping the ovaries and place the healthy uterus of another woman in the place, without it being connected to the ovaries. This "new" uterus can be removed from a family member with the same blood type or donated by another compatible woman, and the possibility of using donated uterus after the death is also being studied.
In addition to the uterus, the recipient should also keep a part of the other woman's vagina to ease the procedure and take medications to prevent rejection of the new uterus.
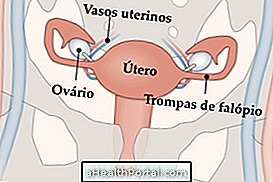

Is it possible to get pregnant naturally after transplantation?
After 1 year of waiting, to know if the uterus is not rejected by the body, the woman can become pregnant through in vitro fertilization, because natural pregnancy becomes impossible since the ovaries are not connected to the uterus.
Doctors do not attach the new uterus to the ovaries because it would be very difficult to make sure there were no scars that would make it difficult to move the egg through the fallopian tubes to the uterus, which could hinder pregnancy or facilitate the development of an ectopic pregnancy, for example .
How In Vitro Fertilization Is Done
For in vitro fertilization to occur, before transplantation of the uterus, doctors remove mature eggs from the woman so that after being fertilized in the laboratory, they can be placed inside the transplanted uterus, allowing pregnancy. The delivery should be performed by caesarean section.
Transplantation of the uterus is always temporary, leaving only enough time for 1 or 2 pregnancies to prevent a woman from having to take her immunosuppressive medications for life.
Risks of Uterine Transplantation
Although it may make pregnancy possible, transplantation of the uterus is very risky, as it can lead to various complications for the mother or the baby. Risks include:
- Presence of blood clots;
- Possibility of infection and rejection of the uterus;
- Increased risk of preeclampsia;
- Increased risk of miscarriage at any stage of pregnancy;
- Restriction of baby's growth and
- Premature birth.
In addition, the use of immunosuppressive drugs, to prevent organ rejection, may cause other complications, which are not yet fully understood.