The T4 exam aims to evaluate the functioning of the thyroid through the dosage of the total T4 hormone and free T4.
Under normal conditions, the hormone TSH stimulates the thyroid to produce T3 and T4, which are hormones responsible for aiding metabolism, providing the energy needed for the correct functioning of the body. T4 is almost completely conjugated to proteins so it can be transported into the bloodstream to various organs and can perform its function.
This test may be recommended by your doctor for routine tests, but it is best done when the person has symptoms of hypo- or hyperthyroidism, for example, or when there is a change in TSH. See what the TSH test is for and the reference values.
How is the exam done?
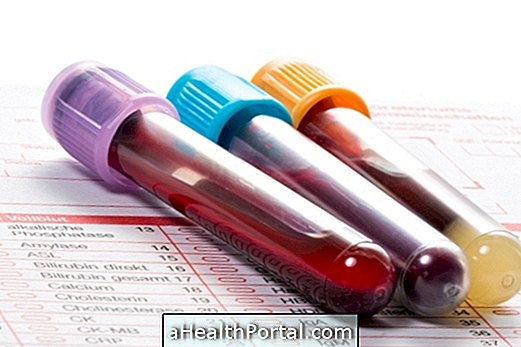
The test is done with a blood sample and no preparation is necessary before performing it. However, if the person is taking any medicine that interferes with the thyroid, he / she should tell the doctor to take this into consideration at the time of the analysis.
The collected blood sample is sent to the laboratory, where the free and total T4 dosage is done. The normal values of free T4 are between 0.7 - 1.5 ng / dL, while the normal values of total T4 vary according to age:
| Age | Normal values of total T4 |
| 1st week of life | 15 μg / dL |
| Until the 1st month | 8.2 - 16.6 μg / dL |
| Between 1 and 12 months of life | 7.2 - 15.6 μg / dL |
| Between 1 and 5 years | 7.3 - 15 μg / dL |
| Between 5 and 12 years | 6.4 - 13.3 μg / dL |
| From 12 years old | 4.5 - 12.6 μg / dL |
High or decreased T4 values may indicate hypo or hyperthyroidism, thyroid cancer, thyroiditis, goiter and female infertility, for example. In addition, decreased free T4 values may indicate poor nutrition or Hashimoto's thyroiditis, for example, which is an autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation of the thyroid leading to hyperthyroidism followed by hypothyroidism. Learn about Hashimoto's thyroiditis and how to treat it.
When to do
The T4 exam is usually requested by the endocrinologist in situations such as:
- Impaired TSH result;
- Weakness, decreased metabolism and fatigue, and may be indicative of hypothyroidism. Here's how to identify and treat hypothyroidism;
- Nervousness, increased metabolism, increased appetite, and may indicate hyperthyroidism. Learn about the symptoms of hyperthyroidism;
- Suspected thyroid cancer;
- Research causes female infertility.
From the evaluation of the results of the examination and the symptoms of the person, the endocrinologist can define the diagnosis and the best form of treatment, thus normalizing T4 levels. See other tests that are essential for thyroid screening.
What is total T4 and free T4?
Both free T4 and total T4 are used to assess thyroid function, that is, to check whether the gland produces normal and sufficient amounts of hormones to provide energy for the body's metabolic activities. Less than 1% of T4 is in free form, and it is this form that is metabolically active, that is, it has function. Protein-bound T4 has no activity, is only carried in the bloodstream to the organs, and when necessary, is separated from the protein to have activity.
The total T4 corresponds to the total amount of hormone produced, being evaluated both the amount that is conjugated to proteins and that which is free circulating in the blood. However, the total T4 dosage may be somewhat unspecific, as there may be interference with the proteins that the hormone can bind.
Free T4, on the other hand, is already more specific, sensitive and allows better evaluation of the thyroid, since only the amount of hormone that is functional and active in the body is dosed