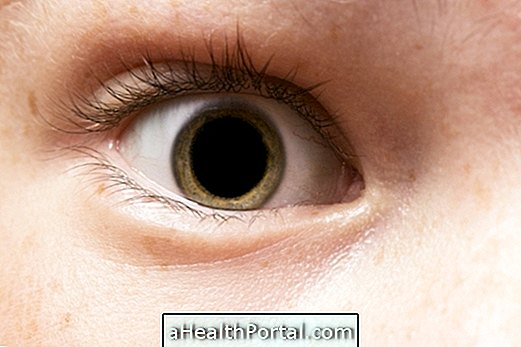
The dilated pupil, whose technical name is mydriasis, usually does not pose major problems, being only situational and returning to normal shortly thereafter. However, when pupils delay to return to normal, have different sizes or do not react to light stimuli, it can be a sign of more serious conditions, such as heart attack, brain tumor or breathing problems, for example.
The pupils are structures present in the eyes responsible for regulating the entrance of light and guarantee quality and clarity of vision. In normal situations, the pupil reacts to light stimuli by dilating or contracting according to the amount of light.
Main causes
The pupil may dilate in a variety of situations, most often being completely normal. Some situations that can lead to dilation of the pupils are:
- Use of eye drops, especially those used to make the ophthalmological exams, which are used precisely to dilate the pupils and allow the visualization of the fundus of the eye. Learn more about eye examination;
- Decreased amount of oxygen in the brain, which may be due to breathing problems or poisoning, for example;
- Situations that cause pain, which leads to dilation of the pupil according to the intensity of pain;
- Situations of stress, tension, fear or shock ;
- Damage to the brain, either due to accidents or due to the presence of brain tumor - see what are the main symptoms of brain tumor;
- Use of drugs, such as amphetamine and LSD, for example, which in addition to causing psychological and behavioral changes, can also lead to physical changes. Find out what signs may indicate drug use;
- Physical attraction, which is often associated with dilation of the pupils, however dilation can not be used as a measure of sexual desire or attraction.
In addition, the pupils may dilate when you are making a lot of effort to think or are too concentrated to perform a certain task, for example. As soon as the situation that demands focus and attention has an end or when you lose interest, the pupils return to normal.
When can it be dangerous?
Dilation can be a more serious problem when the pupil does not respond to stimuli and remains dilated, this being called a paralytic mydriasis, which can occur in one or both eyes. Therefore, if the pupil does not return to normal after a few hours or days, it is important to seek medical help, as it can be respiratory problems, head trauma, heart attack or aneurysm, for example.
It is common that after the accidents the evaluation of the pupils is made, which is done by stimulating the pupils by a flashlight. This is to check if the pupils react to the light stimulus and thus to be able to indicate the general state of the person. If there is no reaction, they remain dilated or have different sizes, it can mean head trauma or increased intracranial pressure, for example.
How is the treatment done?
The dilated pupil is usually not severe, requiring no treatment. Generally the dilated pupil returns to normal in a short time, but in the case of dilation of the pupil for ophthalmic exams it may take a few hours.
However, when it occurs due to heart or brain problems, for example, it is up to the cardiologist or neurologist to identify the cause and begin treatment.