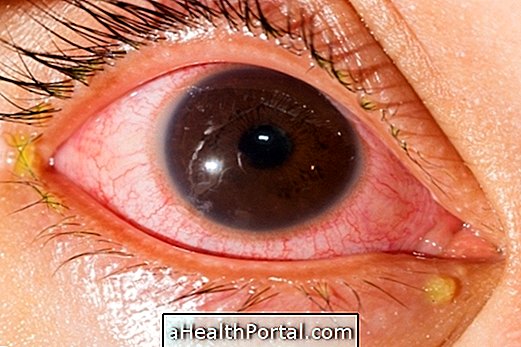
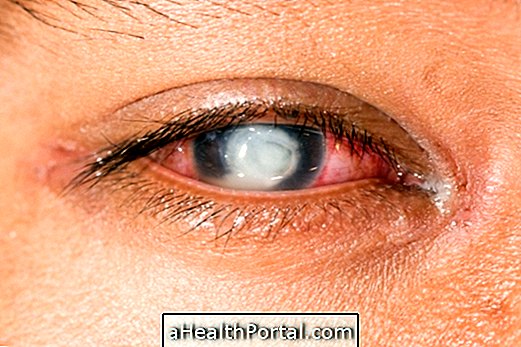
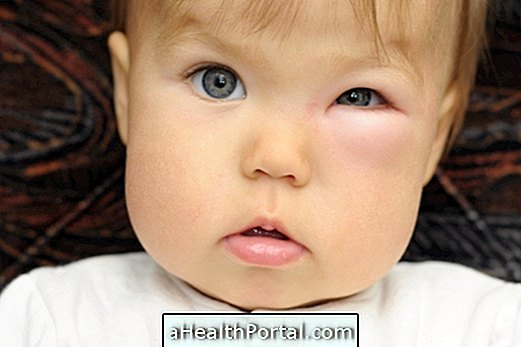
Cellulitis of the orbit is the inflammation or infection that is located in the eye, which is the cavity of the face where the eye and its attachments, such as muscles, nerves, blood vessels and lacrimal apparatus, are inserted, reaching its inner orbital part, or periorbital, in the region of the eyelids.
Although not contagious, this disease is caused by a bacterial infection, by bacteria that colonize the skin after a blow or by the extension of a nearby infection, such as by sinusitis, conjunctivitis or dental abscess, for example, and causes symptoms such as pain, swelling, dislocation, and difficulty moving the eye.
It is more common in infants and children around 4 to 5 years of age, due to the greater delicacy of the structures that surround the eye, such as a thinner porous bone wall. Treatment should be done as soon as possible with antibiotics in the vein and, if necessary, surgery to remove secretion and tissues, preventing the infection from spreading to deeper regions, and may even reach the brain.
Main causes
This infection happens when a microorganism reaches the ocular region, mainly by the enlargement of a neighboring infection, such as:
- Injury in the ocular region;
- Bug bite;
- Conjunctivitis;
- Sinusitis;
- Dental abscess;
- Other infections of the upper airways, skin or lacrimal canals.
The microorganisms responsible for the infection depend on the patient's age, health status and previous infection, with the main ones being Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes and Moraxella catarrhalis.
How to confirm
To diagnose ocular cellulitis, the ophthalmologist will observe the main signs and symptoms, but may also ask for tests such as hemogram and blood culture, to identify the degree of infection and the microorganism, as well as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the region of the orbits and face, to identify the extent of the lesion and exclude other possible causes.
Also check out what are the main causes of eye swelling.
Most Common Symptoms
The symptoms of cellulitis in the eye include:
- Swelling and redness of the eyes;
- Fever;
- Pain and difficulty in moving the eye;
- Ocular displacement or protrusion;
- Headache;
- Vision change.
As the infection worsens, if it is not treated rapidly, it can become severe and reach neighboring regions and cause complications such as orbital abscess, meningitis, loss of vision due to involvement of the optic nerve, and even generalized infection and death.
How is the treatment done?
To treat cellulitis in the eye, it is necessary to receive antibiotics in the vein, such as Ceftriaxone, Vancomycin or Amixicillin / Clavulonate, for example for about 3 days, and continue oral antibiotic treatment at home, complementing a total of 8 to 20 days of treatment, which varies according to the severity of the infection and whether there are other associated infections, such as sinusitis.
It is also necessary to use analgesic and antipyretic medicines for pain relief and fever. In addition, surgery for drainage may be indicated in cases of orbital abscess, compression of the optic nerve or when there is no improvement in the condition after initial treatment.