Plastic surgery can be dangerous because there may be some complications such as infection, thrombosis or rupture of the stitches. But these complications are more frequent in people who have chronic diseases, anemia or taking anticoagulants like Varfina and Aspirin, for example.
In addition, there is a greater chance of complications when the surgery lasts more than 2 hours, in case of general anesthesia or when having a big surgery, such as abdominoplasty followed by breast prosthesis and gluteal graft, for example.
The best way to reduce the risk of complications due to plastic surgery is to perform the procedure in a clinic or hospital with a plastic surgeon who is a member of the Brazilian Society of Plastic Surgery and follow all your recommendations in the pre- and postoperative period.
7 Major Complications of Plastic Surgery
Some of the major risks of plastic surgery include:
1. Bruise and purple bruises
The development of a hematoma is the most common complication of plastic surgery, which occurs due to the accumulation of blood in the operated region, causing swelling and pain. In addition, purple spots may also appear because the blood vessels rupture during surgery.
These complications can arise in all plastic surgeries, being frequent in surgeries to correct the eyelids such as blepharoplasty, facelift or liposuction.
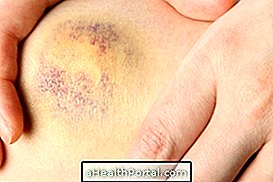

Although they are common and low risk complications, they are in most cases easily treated with ice or the application of ointments such as Thrombofob or Hirudoid, for example, and disappear slowly up to 2 weeks after surgery. Here are some simple tips for getting bruises.
2. Accumulation of liquid
When there is swelling, reddened skin, pain and buoyant sensation at the scar site, a complication called a seroma may be developing.
To avoid this complication it is essential to use a strip, bandage or compressive dressing in the postoperative period, to stand and use a drain to remove excess fluid. In some cases, it may be necessary for a nurse to remove the liquid with a syringe to facilitate recovery.
3. Opening of points

The opening of the stitches or staples can cause dehiscence, which is when separation of the borders of the tissues that were united and the risk of developing an infection is increased and the healing time increases.
This complication can arise when the person performs excessive movements in the postoperative not fulfilling the rest recommended by the doctor and is more common in surgeries in the belly, like abdominoplasty.
4. Infection
The risk of infection is more common around the scar, but an internal infection can also occur, causing symptoms such as swelling, pain, fever and pus. In addition, in the case of surgeries where silicone prostheses are applied, such as augmentation mammoplasty, prosthesis rejection can occur, resulting in infection that must be treated with the use of medications indicated by the physician.
5. Thrombosis

When thrombus or clot formation occurs it is normal to feel swelling and intense pain in the legs, especially in the calf, in addition to shiny and purplish skin, and in the case of not being treated quickly the clots can move to the lungs causing pulmonary embolism, a serious situation that can be fatal.
To avoid this complication it is essential to take anticoagulant medicines, such as Enoxaparin, and to move your feet and legs even while lying down, at rest. See other ways that can help prevent thrombosis of the legs.
6. Deformed scars


The appearance of thick, deformed and keloid scars can occur after any plastic surgery but are more common the larger the scar. In addition, it can also develop nodules under the skin that is caused by the formation of a hard tissue in place, which pulls the skin.
In some cases, retractable scarring may occur, which is when the skin pulls inward and creates a hole in the operated region. The best ways to treat deformed scars are through aesthetic physiotherapy sessions or by doing a new plastic surgery to correct the scar.
7. Decreased sensitivity
The loss of sensitivity of the operated region and on the scar may occur due to the swelling of the region, but this sensation diminishes with the passage of time.
In addition to these 7 complications of plastic surgery necrosis, which is the death of tissues due to lack of blood and oxygen and organ perforation, however, these complications are rarer and are related to inexperience of the plastic surgeon.
Main consequences of anesthesia
All plastic surgeries are performed under anesthesia to block the pain and allow the doctor to perform the procedure correctly. But anesthesia can also cause other complications.
Risks of general anesthesia
The main reactions caused by general anesthesia, which is when the patient takes sleeping pills deeply and breathe with the aid of appliances, include nausea and vomiting, urinary retention, low blood pressure, dizziness, tiredness, excessive drowsiness, tremors and headache. In more severe cases, breathing difficulties, infarction or even death may occur, but this is rare.
To relieve the symptoms that general anesthesia can cause, the nurse often gives remedies to relieve vomiting and decrease pain, put a bladder catheter to help urinate without difficulty, but it is also important to sleep and rest.
Risks of epidural anesthesia or spinal anesthesia
The epidural anesthesia that is applied to the spine leads to loss of sensitivity of a part of the abdomen, hip and legs keeping the person awake. Its consequences involve the decrease of the sensitivity of the legs by excessive time, which increases the risk of fall and burn. In addition, pressure relief and back pain may occur at the site of the bite.
Risks of local anesthesia
Local anesthesia is one that causes fewer side effects, however, it can cause swelling, decreased sensitivity and hematoma at the site where the injection was given.
Who is more likely to develop complications?
All individuals can develop complications during or after plastic surgery, but patients who are more likely to have problems include:
- Age greater than 60 years;
- Chronic diseases such as hypertension, diabetes or sleep apnea;
- Weak immune system, such as HIV +, cancer or hepatitis;
- People who take anticoagulants or have problems such as varicose veins, thrombosis, anemia or difficulty in clotting or scarring;
- BMI greater than 29 and high amount of abdominal fat.
In addition, smokers or drug users are also more likely to have complications, and when they have had complications in other surgeries the risk is even greater.
How to reduce the risks of plastic surgery
To avoid complications during surgery or in the postoperative period it is essential before performing the surgery:
- Perform medical exams such as a complete blood test and electrocardiogram. See the top exams you should do.
- Reduce the number of cigarettes you smoke or stop smoking at least 1 month before surgery to prevent pulmonary embolism;
- Avoid taking the pill 1 month before surgery, especially if the surgery lasts longer than 4 hours, to decrease the risk of thrombosis;
- Failure to take some medicines, such as aspirin on the advice of the doctor to avoid complications;
- Take antibiotics before surgery, on a doctor's recommendation.
To minimize these dangers the individual should always choose to choose a plastic surgeon who is skilled and reliable and choose a hospital or clinic that has a good recognition.