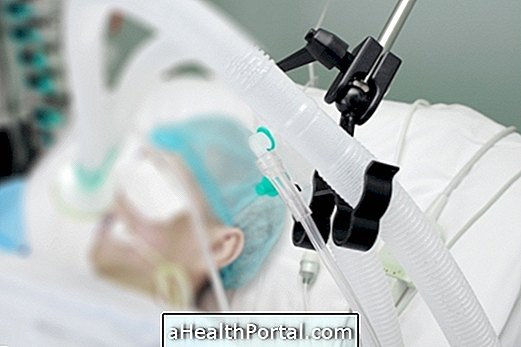
The coma corresponds to the state of unconsciousness in which all functions of the organism are reduced, although the brain continues to produce electrical signals capable of maintaining vital functions, such as breathing, for example. Coma can occur due to several situations, such as severe head bumps, infections and excessive consumption of alcohol, for example, being called an alcoholic coma in this case. Know the warning signs of the alcoholic coma.
Coma can be classified according to the Glasgow Coma Scale, where the medical staff assesses the person's motor, verbal and ocular abilities at the time, and can indicate the person's levels of consciousness and thus prevent possible sequelae and establish the best treatment.
Main causes
The causes of coma are still not fully understood, and may have several causes, and may be caused by the use of a particular medication during hospitalization, known as induced coma, but can also happen naturally as a consequence of:
- Toxic effect of any drug or substance, such as illicit drugs or alcohol, for example;
- Infections, such as meningitis or sepsis, for example, which can lower the person's levels of consciousness due to the involvement of various organs;
- Cerebral haemorrhage, which is characterized by bleeding in the brain due to rupture of a blood vessel;
- Cerebral Vascular Accident, which corresponds to the interruption of blood flow to some region of the brain;
- Cranial trauma, which is an injury to the skull caused by concussion, cuts or bruises, and that when there is impairment in the brain, it is called cranio-encephalic trauma;
- Lack of oxygenation in the brain due to severe lung diseases or excessive inhalation of carbon monoxide, such as automobile engine smoke or home heating system, for example.
In addition, coma may be a result of hyper or hypoglycemia, hyper or hypothermia, and epileptic seizures lasting only a few minutes in this case. Coma is usually a situation that precedes brain death, in which the brain no longer emits electrical signals to the body. Know the difference between brain death and coma.
Glasgow Coma Scale
The Glasgow Coma Scale is used by the medical staff to assess the person's overall condition and thereby define the best therapeutic strategy. This scale is based on the person's response to motor, verbal, and ocular stimuli, and a score is assigned according to the person's coma response. From the sum of the points, it is possible to verify the coma stage that the patient is in.
1. Visual stimulation
| answer | Punctuation |
| Does not open the eyes | 1 |
| Open your eyes after fingertip stimulation | 2 |
| Opens eyes due to auditory stimulus | 3 |
| Open your eyes spontaneously, even before any kind of stimulation | 4 |
2. Motor stimulus
| answer | Punctuation |
| There is no movement of upper or lower limbs | 1 |
| Extension of the upper limb to the level of the elbow | 2 |
| Abnormal flexion of the upper limb at the level of the elbow | 3 |
| Can flex rapidly upper limb at elbow level | 4 |
| Can raise hand above collarbone due to stimulation of the head or neck | 5 |
| Complies with at least 2 motor actions | 6 |
3. Verbal stimulation
| answer | Punctuation |
| do not speak | 1 |
| Only emits moans | 2 |
| Speak disconnected words or out of context | 3 |
| It speaks in an unguided but coherent way | 4 |
| Usually responds to issues related to name, location, and date | 5 |
From the patient's evaluation according to the Glasgow coma scale, it is possible to determine the patient's coma according to the score obtained in:
- Normal, when the score is equal to 15;
- Eat light, when the score is between 11 and 14;
- Eat intermediate, when the score is between 7 and 10;
- Eat deep, when the score is less than 6, and may also be indicative of vegetative state.
In addition to these criteria, the evaluation of the pupil reaction against light stimuli was also added, and scores were also attributed:
- 0, if the two pupils react to the light stimulus;
- 1, if only one pupil reacts;
- 2, when no pupils react to light.
The score obtained in the analysis of the pupil response is subtracted from the result obtained from the analysis of the visual, motor and verbal stimuli, resulting in a more accurate evaluation of the general state of the patient.
Caring for the person in coma
The person usually stays in a coma for a few weeks without having to use sedative medication during hospitalization, this being done according to the state of health of the person.
It is recommended that the person in a coma have their position changed by the nursing team every 2 to 4 hours to avoid the formation of wounds or ulcers, for example. In addition, it should be constantly monitored by the medical team so that its evolution can be evaluated, as well as the monitoring of feeding, which is done by means of a catheter, and elimination of urine and feces.