After delivery, the woman should be aware of some symptoms that may indicate diseases that must be identified and properly treated by the physician to ensure their health and well-being. Some symptoms that should not be ignored are fever, loss of large amount of blood, runny nose, fever and shortness of breath.
With the onset of any of these symptoms, the woman should go to the hospital quickly, to be evaluated and treated appropriately, as these symptoms may indicate serious problems such as placental retention, thrombosis or embolism, for example.

5 common postpartum changes
Here we indicate the symptoms and treatments of some of the most common situations after childbirth. Are they:
1. Postpartum haemorrhage
The loss of large amounts of blood through the vagina usually occurs within the first 24 hours after the birth of the baby, however, this change can also occur up to 12 weeks after normal delivery or cesarean due to abrupt detachment of placental remnants or uterine rupture.
Postpartum haemorrhage is characterized by the loss of too much blood suddenly and intense vaginal bleeding, and it is necessary to change the absorbent every hour. See when to worry about postpartum bleeding.
What to do: You should go to your doctor immediately, as you have to use medicines that promote uterine contraction. The doctor may also perform a vigorous massage in the uterus until the uterus contracts completely by resolving the bleeding. Learn more about postpartum haemorrhage.
Placental retention
After any kind of delivery, small remains of the placenta may remain stuck in the uterus causing infection. In this case there is a proliferation of bacteria inside the uterus, being potentially serious, since these bacteria can reach the bloodstream and cause septicemia, a very serious situation that puts the woman's life at risk. Learn how to identify and treat placental remnants in the uterus.
Placental retention is characterized by the presence of foul smelling discharge, fever above 38 ° C, and loss of dark, viscous blood even after it is lighter and more fluid.
What to do: The doctor may prescribe remedies for uterine contraction and use of antibiotics, but often the placental remains are removed only through uterine curettage, a simple surgical procedure that can be done in a doctor's office, but in this case normally is done in the hospital. Understand what uterine curettage is and how it is done.
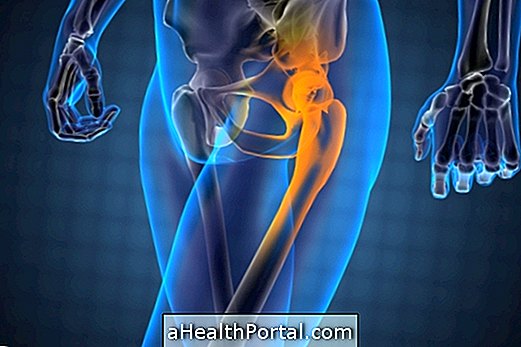
3. Venous thrombosis
The fact that many hours lie down, or in labor, and due to the presence of small emboli of blood or gases, thrombi can form that prevent the correct passage of blood through the blood vessels of the leg. If the thrombus travels, it may reach the heart or the lung, causing further complications. Thrombosis is characterized by swollen legs, calf pain, rapid heartbeat, and shortness of breath. Learn how to identify thrombosis.
What to do: Your doctor may recommend the use of anticoagulant medicines to ease the passage of blood such as warfarin and heparin.

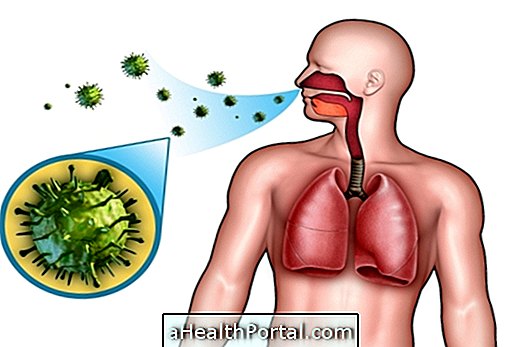
4. Pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism occurs when a plunger or clot reaches the lungs, compromising its irrigation. With reduced blood circulation, this organ is compromised and symptoms of shortness of breath, breathing difficulty, chest pain, increased heart rate, low blood pressure and fever appear. Understand what pulmonary embolism is.
What to do: The doctor may prescribe analgesics and anticoagulants to facilitate the passage of blood and use of oxygen mask, and in some cases surgery may be necessary. See how the treatment for pulmonary embolism is done.
Hypovolemic shock
Hypovolemic shock, also known as hemorrhagic shock, is a consequence of postpartum haemorrhage, since this condition occurs when the woman loses a lot of blood, the heart being unable to properly pump the blood to the whole body.
This type of shock is characterized by palpitations, dizziness, sweating, weakness, a very strong and persistent headache, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, and put a woman's life at risk. Learn about first aid for hypovolemic shock.
What to do: Requires blood transfusion to replenish the amount of blood needed to maintain the function of all organs and systems. It may take more than 1 transfusion, plus the use of iron supplements for a few weeks. After the hemogram indicates the presence of hemoglobin and ferritin at normal values, the treatment may be terminated.
What doctor to look for
The best doctor to treat postpartum changes is still the obstetrician, but the most important thing is to go to the hospital as soon as you notice any of these symptoms, telling them when they came up and how intense they are. The doctor may order tests such as a blood test and transvaginal ultrasound, for example to identify the cause and start treatment.
The woman should bring a companion and it may be more peaceful to leave the baby at home with the nanny or with another person who can care for him until she can return home to take care of him.