Catheterization is a medical procedure in which a plastic tube, called a catheter, is inserted into a blood vessel, organ or body cavity in order to facilitate the passage of blood or other fluids.
The procedure is performed according to the clinical conditions of the patient, and can be done in the heart, bladder, navel and stomach. The most frequently performed type of catheterization is cardiac catheterization, which is performed to aid in the diagnosis and treatment of heart disease.
Like any other medical procedure, catheterization presents risks, which vary according to the place of placement of the tube. Therefore, it is important that the person be accompanied by a nursing team in order to avoid any complications.
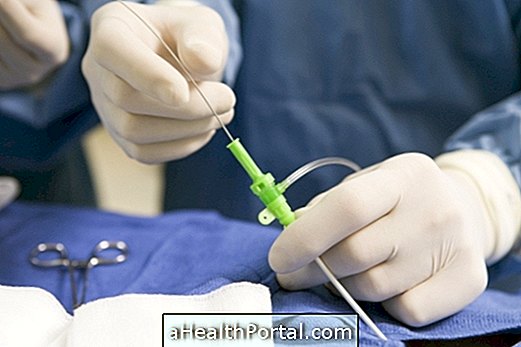
Types of catheterization
The catheterization is performed according to the needs of the patient, the main ones being:
Cardiac catheterization
Cardiac catheterization is an invasive, rapid and accurate medical procedure. In this procedure, the catheter is inserted through an artery, a leg, or an arm into the heart.
Catheterization is not a major surgical intervention, but is done in the hospital, on a specific examination machine that emits radiation (more than ordinary radiographs) and where venous contrast is used. Therefore, cardiac monitoring is required throughout the examination so that the heart is controlled through the electrocardiogram. Almost always, it is performed with local anesthesia associated or not, with sedation.
Depending on the purpose, catheters may be used to measure pressure, look inside the blood vessels, widen a heart valve, or unclog a blocked artery. It is also possible, through the use of instruments introduced through the catheter, to obtain tissue samples from the heart for biopsy. Learn more about cardiac catheterization.
Bladder Catheterization
Bladder catheterization consists of the introduction of a catheter through the urethra, which reaches the bladder with the intention of emptying it. This procedure can be performed in the preparation of surgeries, in the surgical post or to check the amount of urine produced by the person.
This type of catheterization can be performed by means of relief probes, which are used only for rapid bladder emptying, without the need to maintain the implanted catheter, and may also be of the bladder probing type, which is characterized by the placement of a catheter catheter coupled to a collection bag that stays for a certain time collecting the person's urine.
Umbilical catheterization
The umbilical catheterization consists of introducing the catheter through the navel to measure blood pressure, check blood gases and other medical procedures. It is usually performed on preterm infants during the time they are in the neonatal intensive care unit, and is not a routine procedure, since it has risks.
Nasogastric catheterization
Nasogastric catheterization is characterized by the introduction of a plastic tube, the catheter, into the person's nose and into his stomach. This procedure can be done to feed or withdraw fluids from the stomach or esophagus. It should be introduced by a qualified professional and the position of the catheter should be confirmed with a radiograph.
Risks of catheterization
The person who underwent catheterization should be accompanied by the nursing team with the aim of avoiding hospital infections and complications, which vary according to the type of catheterization performed:
- Allergic reactions, arrhythmia, bleeding and heart attack, in the case of cardiac catheterization;
- Urinary tract infections and trauma to the urethra in the case of bladder catheterization;
- Hemorrhage, thrombosis, infections and increased blood pressure, in the case of umbilical catheterization;
- Haemorrhage, aspiration pneumonia, lesions in the esophagus or stomach, in the case of nasogastric catheterization.
The catheters are usually changed periodically, and the site is always cleaned.