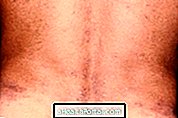
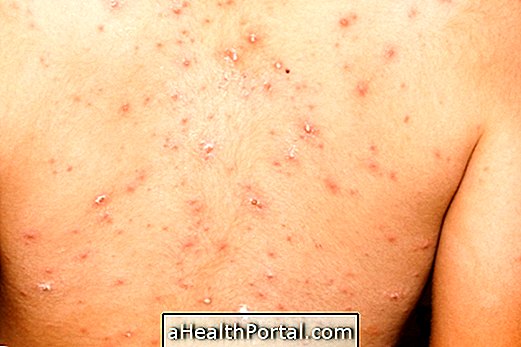
Erythema nodosum is a dermatological inflammation, characterized by the appearance of painful nodules under the skin, about 1 to 5 cm, which are reddish and usually located in the lower legs and arms.
However, there may be other symptoms such as:
- Joint pain;
- Low fever;
- Enlargement of the lymph nodes;
- Tiredness;
- Loss of appetite.
This change can affect people of all ages, being more common from 15 to 30 years. Symptoms usually go away in 3 to 6 weeks, but in some people they may stay longer, up to 1 year.
Erythema nodosum is a type of panniculitis, and is considered a symptom of some diseases, such as leprosy, tuberculosis and ulcerative colitis, but it can also be caused by an allergic reaction to certain drugs.

How to diagnose
The diagnosis can be made by a dermatologist by assessing the symptoms and physical examination of the person, and is confirmed by biopsy of a nodule.
Then the treatment is done according to the cause of erythema nodosum, plus the use of anti-inflammatory and resting to relieve symptoms. Learn how treatment for erythema nodosum is done.
Main causes
The inflammation that causes erythema nodosum occurs due to immune reactions of the body, caused by:
- Infections with bacteria, fungi and viruses such as pharyngitis and erysipelas caused by streptococcal bacteria, mycoses caused by fungi, viruses such as mononucleosis or hepatitis, and contagion by mycobacteria, such as those causing tuberculosis and leprosy;
- Use of some medicines, such as penicillin, sulfa and contraceptive;
- Autoimmune diseases, such as lupus, sarcoidosis and inflammatory bowel disease;
- Pregnancy due to hormonal changes of the period;
- Some cancers, such as lymphoma.
However, there are people in whom the cause may not be found, and in these cases it is called idiopathic erythema nodosum.