The positive Schiller test means that cellular changes have been found in the inner vagina, and may suggest the presence of benign changes, such as poorly placed IUDs, some inflammation, condyloma, syphilis, HPV, or even cervical cancer .
However, the Schiller's test may give a false positive result, and so the pap smear is usually requested instead as a way of investigating cervical cancer because it gives clearer and more concrete results.
Another test similar to this is the acetic acid test where the same principle of coloration of the vagina and cervix is used, in which case the region should be whitish. In places where white is most evident there are signs of cellular changes. This test is particularly indicated for women who have iodine allergy, and can not take the Schiller test.

What is it and what is it for?
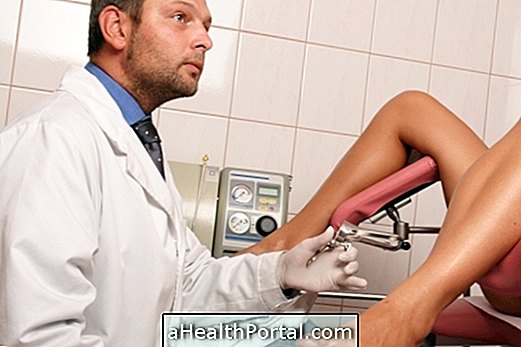
The Schiller test is a diagnostic test consisting of the application of an iodine solution (Lugol) throughout the internal region of the vagina and cervix. This solution reacts with the cells in the region and when they appear brown after application, the result is said to be normal. In cases where the solution can not color some specific areas, it means that there is some change in these areas.
This test is performed on all sexually active women as a routine examination and in those who present with some symptom such as pain, discharge or bleeding after sexual intercourse. In cities with few resources, this test can also be used to screen for cervical cancer. The examination can also be done immediately during a biopsy to make it clear where the tissue should be taken for analysis.