Prostate biopsy is an examination done when the PSA value in the blood test is high or when changes in its size or shape are found during the rectal examination, being definitive to mislead or confirm a diagnosis of prostate cancer.
Prostate biopsy does not hurt, but it can be uncomfortable and, for this reason, it is usually done under local anesthesia or mild sedation. However, after the examination it is possible that the man feels some burning in the region, but that it passes in a few hours.
When to Get a Prostate Biopsy
This test is indicated when the prostate appears hard or enlarged and when the PSA result is:
- PSA above 4 ng / mL at any age:
- PSA above 2.5 ng / mL in patients up to 55 years of age;
- PSA density above 0.15 ng / mL;
- PSA velocity above 0.75 ng / mL / yr.
The examination should be repeated when the doctor is not satisfied with the result of the 1st biopsy, especially if there is:
- PSA persistently elevated or elevated and with a rate of> 0.75 ng / mL / year;
- High-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (NIP);
- Atypical proliferation of small acini (ASAP).
Watch the following video and learn about other exams the doctor can perform:

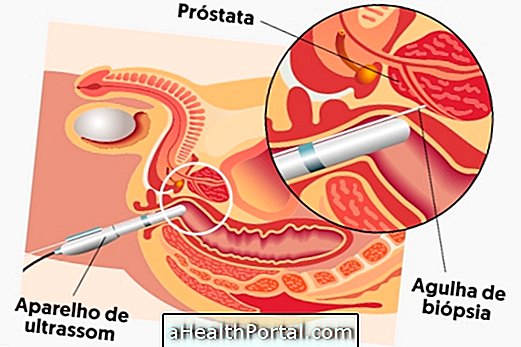
How is prostate biopsy done?
The biopsy is done with the man lying on his side, with his legs folded, properly sedated. The doctor then briefly evaluates the prostate by performing the rectal examination, and after this initial evaluation, the doctor inserts an ultrasound device into the patient's anus, which guides a needle to the prostate.
This needle pierces the intestine and collects several pieces of tissue from the gland, and the regions around it, which will be analyzed in the laboratory for cells that may indicate the presence of cancer.
What is the prostate biopsy price?
The price of prostate biopsy ranges from 200 to 500 reais, depending on the location selected. When cancer is suspected, this test can be done free of charge by the SUS, but its marking can be delayed.
How to prepare for the biopsy
Biopsy preparation is important to avoid complications and usually includes:
- Take the antibiotic prescribed by the doctor for about 3 days before the test;
- Complete at least 6 hours of fasting;
- Do a bowel cleansing before the exam;
- Urinate a few minutes before the procedure;
- Bring a chaperone to assist in returning home.
After prostate biopsy, the man should also take the prescribed antibiotics, eat a light diet in the first few hours, avoid physical exertion in the first 2 days and maintain abstinence for 3 weeks.
Understanding the result of the biopsy
The results of prostate biopsy may be:
- Positive: indicates the presence of cancer developing in the gland;
- Negative: the cells collected did not change.
When the result of the prostate biopsy is negative the doctor may ask to repeat the examination to certify the results when he suspects that the result is not correct. This new examination should be done in 3-4 weeks.
What are the possible risks of biopsy
Since it is necessary to pierce the intestine and remove small pieces of the prostate, there is a risk of some complications such as:
1. Pain or discomfort
After the biopsy, some men may experience mild pain or discomfort in the region of the anus due to scarring of the bowel and prostate. If this happens, your doctor may advise you to use some mild analgesics such as Paracetamol. Usually, the discomfort disappears within 1 week after the examination.
2. Bleeding
The presence of a slight bleeding in the underwear or toilet paper is completely normal during the first 2 weeks, even in semen. However, if the amount of blood is very high or disappears after 2 weeks, it is advised to go to the doctor to see if there is any bleeding.
3. Infection
Since the biopsy causes a wound in the intestine and prostate, there is an increased risk of infection, especially due to the presence of various types of bacteria in the intestine. For this reason, after the biopsy the doctor usually indicates the use of an antibiotic.
However, there are cases where the antibiotic is not enough to prevent infection, so if you have symptoms such as fever above 38 ° C, severe pain or strongly smelling urine, it is advisable to go to the hospital to see if there is any infection and initiate appropriate treatment.
4. Urinary retention
Although it is rarer, some men may get urinary retention after biopsy due to inflammation of the prostate, caused by the removal of pieces of tissue. In these cases, the prostate ends up compressing the urethra, making it difficult to pass urine.
If this happens, you should go to the hospital to remove urine accumulation from the bladder, which is usually done by placing a bladder catheter. Understand better what a bladder catheter is.
5. Erectile dysfunction
This is the rarest complication of the biopsy but usually disappears within 2 months after the examination. In most cases, the biopsy does not interfere with the ability to have intimate contact.