The scalded skin syndrome is a contagious disease consisting of a skin reaction to a cutaneous infection caused by some species of bacteria of the genus Staphylococus, which release a toxic substance that promotes skin peeling, leaving it with the appearance of a skin burned.
The treatment consists of the administration of antibiotics and analgesics and the application of moisturizing creams that accelerate the recovery of the skin.
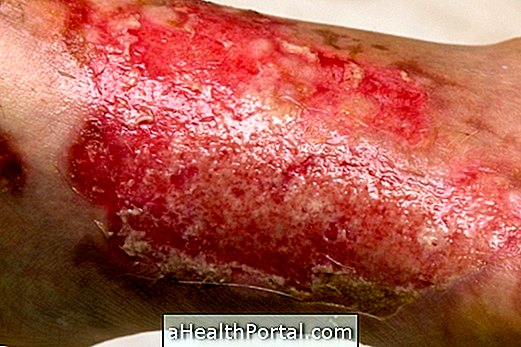
What causes
This disease is caused by some species of bacteria of the genus Staphylococus that enter the body through a cut or a wound and release toxins that hinder the healing of the skin and its ability to maintain the structure, causing the superficial layer to begin to flake
These toxins can spread to the rest of the body through the bloodstream and reach the skin of the whole body, and can even cause widespread infection.
Possible symptoms
Newborns and babies are more susceptible to this syndrome because their immune system and their kidneys are still not well developed. However, it can also appear in older children or in adults, especially those who have a weak kidney function or immune system.
The symptoms of this syndrome begin with the appearance of an isolated wound, which most often occurs in the diaper region or around the rest of the umbilical cord in the case of infants, on the face in cases of older children or even in any part of the in the case of adults.
After 2 or 3 days, the infection site begins to turn red, sore, and the infection begins to spread throughout the body, making it more visible in areas of friction such as buttocks, skin folds, hands or feet, and how the protective barrier of the skin is lost, infection can occur by other microorganisms, which penetrate more easily in the body, and can even spread through the bloodstream causing a generalized infection.
During this process, the upper layer of skin begins to break apart, giving rise to burnt-out skin with easily broken water bubbles, also causing symptoms such as fever, chills, weakness, irritability, appetite, conjunctivitis or even dehydration.

How is the treatment done?
Usually the treatment consists of the administration of antibiotics intravenously and later orally, analgesics like paracetamol and moisturizing creams to protect the new skin that forms. In the case of newborns affected by this syndrome, these are usually kept in an incubator.
The superficial layer of the skin is rapidly renewed, healing in about 5 to 7 days after the start of treatment. However, if not treated in a timely manner, this infection can lead to pneumonia, infectious cellulitis or even generalized infection.
How to avoid
As it is a contagious disease, one of the prevention measures is to avoid contagion, although the person who is infected, only develops the disease if it has a weakened immune system.