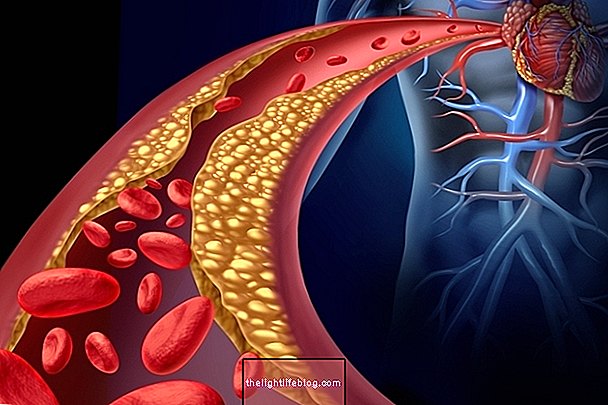
Lipid profile, also known as lipidogram, is the blood test capable of determining the amount of lipids in the bloodstream. Lipids are fat molecules, such as LDL, HDL, VLDL, and triglycerides, which, when they are out of the normal range, pose a major risk for developing cardiovascular diseases such as angina, heart attack, stroke or venous thrombosis.
The lipid profile test is requested by the doctor in order to identify the risk of these diseases and to help guide the ideal treatment for each person as a way to prevent complications to health. To determine the lipid profile a blood test is taken, which may or may not be done fasting. In the complete lipid profile, it is possible to observe the values of:
1. LDL cholesterol
It is considered bad cholesterol, and its values should be kept below 130mg / dl, however, for some people stricter controls such as below 100, 70 or 50mg / dl are required, depending on conditions such as lifestyle, diseases or the presence of other cardiovascular risk factors. Learn more about what bad cholesterol is and what the recommended amount is for each person.

2. HDL Cholesterol
It is good cholesterol, so it is the only one that should be high. It is recommended that its value is above 40mg for men and women as a way to prevent the risk of cardiovascular diseases and for this, it is indicated to perform physical activity and have a diet rich in good fats and fiber present in fish, olive oil, vegetables and seeds, for example. Learn more about what it is and how to raise good cholesterol.
3. VLDL Cholesterol
It is the type of cholesterol that has the function of transporting triglycerides and cholesterol to the tissues of the body, and is part of the non-HDL cholesterol group, so it should be kept low and its values not recommended of 30mg / dL. Learn more about the high cholesterol effects of VLDL.
4. Non-HDL cholesterol
It is the sum of all types of cholesterol except HDL and, like isolated LDL cholesterol, is also considered by doctors to be an important risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, and can be used for monitoring and counseling treatment.
Non-HDL cholesterol should be 30 mg / dL above that considered ideal for LDL, so if the maximum recommended LDL value for a person is 130 mg / dl, non-HDL cholesterol is considered normal if it is up to 160mg / dl.
5. Total Cholesterol
It is the sum of HDL, LDL and VLDL, and it is desirable that it is below 190mg / dL, since when it is high also increases the risk of diseases like heart attack, stroke, angina or pancreatitis, for example. However, it should be borne in mind that if good cholesterol (HDL) is too high, it may increase the value of total cholesterol, so it is always important to compare the values of the complete lipid profile. Learn more about what total cholesterol is and the steps to control it.
6. Triglycerides
Also known as triglycerides, these fat molecules are an important source of energy for the body and muscles; however, when they are elevated in the bloodstream, they can facilitate the buildup of fat in the blood vessels and the development of cardiovascular diseases.
The desirable value of triglycerides in the lipid profile test is lower than 150mg / dl, and the higher the value, the greater the chances of complications. In addition to cardiovascular disease, excessively high triglycerides can also cause pancreatitis. Check for other signs and symptoms of high triglycerides.

When the lipid profile test is indicated
Generally, lipid-lowering is done for adults every 5 years; however, if there is a higher risk for heart disease or if cholesterol is changed in other tests, this range should be lower.
Although this test is usually not ordered for children and adolescents, it can be done in those who are likely to develop heart disease, such as those with genetic diseases of cholesterol, diabetes, high blood pressure or obesity, for example.
What to do when changed
When the lipid profile is altered it is important to perform the treatment, which is guided by the doctor and, preferably, with a follow-up by a nutritionist. The main ways to treat these changes include:
- Changes in diet : Avoid high-fat foods such as fried or fatty meats, and excessive carbohydrates. However, it should never be forgotten that the diet should be balanced, and with the ideal amounts of nutrients for each person, so it is recommended follow-up with a nutritionist, so that you know how to select the food better and in the ideal quantity. Check out, in the following video, tips from our nutritionist on a cholesterol-lowering diet:

- Healthy Living Habits : To lower bad cholesterol and increase good cholesterol, it is recommended to practice regular physical activity at least 3 to 6 times a week with an average of 150 minutes of exercise. It is also important to stop smoking, as this habit influences the drop in good cholesterol;
- Medication use: In many cases the doctor will recommend the use of medications to control cholesterol and triglyceride levels, and some of the major ones include statins for lowering coleterol, such as simvastatin, atorvastatin, or rosuvastatin, for example, or fibrates for triglycerides, such as Ciprofibrate or Bezafibrate, for example. Learn more about cholesterol-lowering medicines and what to do to lower triglycerides.
In addition, to reduce the chances of developing cardiovascular disease, it is also important to control other risk factors, such as controlling blood glucose levels, blood pressure and losing weight, as all these factors contribute to the formation of atherosclerosis in the blood vessels and the disease development.