Cholesterol is a type of fat present in cells, fundamental for the proper functioning of the body. However, having high total cholesterol levels in the blood increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, so it is important that your blood sugar levels are balanced, which can be achieved with a low-fat diet and regular exercise.
However, in people with higher risk factors for developing cardiovascular disease, this control should be more rigorous, so the use of medications such as Simvastatin or Atorvastatin, for example, may be recommended by the doctor.

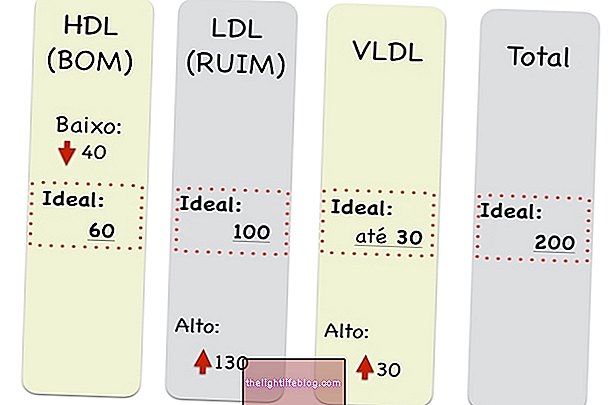
Here's what the proper levels and levels of each type of cholesterol mean:
1. HDL Cholesterol
HDL cholesterol is known as good cholesterol, so it is the only one that should stay high in the bloodstream. It is produced by the body, being essential for the proper functioning of the body, so it is ideal to always have it above 40 mg / dl. To increase the levels of HDL cholesterol in the body, what you should do is to lose weight, adopt a diet low in fat and practicing physical exercises regularly. The HDL reference values are:
| HDL cholesterol (good) | Low: <40 mg / dl for men and women | Ideal: above 40 mg / dl |
Learn About Good Cholesterol In: Good Cholesterol
2. LDL cholesterol
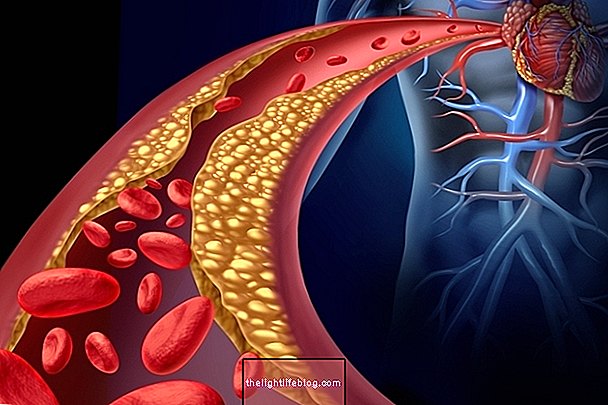
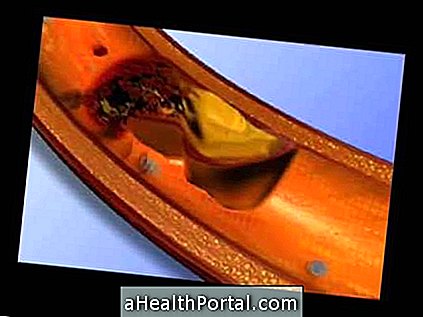
LDL cholesterol is bad cholesterol. It is considered high when it is equal to or greater than 130 mg / dL for most people, however, in some cases, tighter controls are required. When the level of LDL cholesterol is high there begins to be deposition of fat in the walls of blood vessels, forming plaques of fat that, over time, can hinder the passage of blood and lead to a heart attack or stroke, for example.
To lower LDL cholesterol in the blood, you should follow a diet low in sugar and fat and do some physical activity at least 3 times a week, however, when these attitudes alone are not enough, your doctor may recommend the use of medications to reduce their levels. The LDL reference values are:
| Recommended LDL (Bad) Cholesterol | For whom | Examples |
| <130 mg / dl | People with low cardiovascular risk | Young people, without disease or with well controlled hypertension, with LDL between 70 and 189 mg / dl .. |
| <100 mg / dl | People with intermediate cardiovascular risk | People with 1 or 2 risk factors, such as smoking, high blood pressure, obesity, controlled arrhythmia, or diabetes that are initial, mild and well controlled, among others. |
| <70 mg / dl | People with high cardiovascular risk | People with cholesterol plaques in vessels seen by ultrasound, abdominal aortic aneurysm, chronic kidney disease, with LDL> 190mg / dl, diabetes for more than 10 years or with multiple risk factors, among others. |
| <50 mg / dl | People with very high cardiovascular risk | Persons with angina, infarction, stroke or other type of arterial obstruction due to plaques of atherosclerosis, or with any serious arterial obstruction observed in the exam, among others. |
Low, intermediate, high or very high cardiovascular risk are determined by the physician during the visit, after observation of the necessary tests and clinical evaluation. Learn more about this type of cholesterol in: Colestrol LDL.
3. VLDL Cholesterol
VLDL cholesterol carries triglycerides and also increases the risk of heart disease. The VLDL reference value is usually:
| VLDL Cholesterol | High | Low | Ideal |
| above 40 mg / dl | below 30 mg / dl | up to 30 mg / dl |
However, in the last recommendations of the Brazilian cardiology society, the values of VLDL are not considered relevant, with non-HDL cholesterol values higher, whose target should be 30 mg / dl above LDL.
4. Total Cholesterol
Total cholesterol is the sum of HDL, LDL, and VLDL. Having high total cholesterol poses a high risk of cardiovascular disease and therefore, its values should not exceed 190 mg / dl.
Total cholesterol above 190 is less worrisome if LDL levels are normal, but one should take care, such as reducing the intake of high-fat foods to keep cholesterol from being too high and harmful to health. A good tip is to reduce the consumption of red meats. The reference values for cholesterol are:
| Total cholesterol | Desirable: <190 mg / dl |
High cholesterol
High cholesterol is diagnosed on a blood test called lipidogram since it does not usually cause symptoms. When it comes to cholesterol levels, what you should do is follow a low-fat, low-sugar diet and exercise regularly.
If you do not respond to the initial treatment, your doctor may recommend the use of cholesterol medicines, such as statins. Learn more about the best cholesterol-lowering medicines.
Also, some tips on what you can eat to lower your high cholesterol are:
- Fruits, vegetables, vegetables, lean meats such as chicken breast and fish fillet and light dairy. A great home remedy for lowering the blood cholesterol ratio is to take 1 cup of orange juice beaten with eggplant daily.
See home remedies for lowering bad cholesterol in the following video: