Yellowish stools may be the result of problems like intestinal infection, poor digestion, celiac disease or due to a high fat diet.
Observing the color, shape, and smell of feces is important in identifying health problems, as they change according to how the bowel and other organs work.
The following are the main causes of the appearance of yellowish stools.
1. Fat-rich diet
Eating too much fat hinders digestion and speeds up the intestinal transit, especially in people who eat a balanced diet.
What to do: Reducing the amount of fat and processed foods from the diet will help regulate stool color, which should improve after 2 or 3 days. However, if the problem persists any longer, other causes should be investigated.
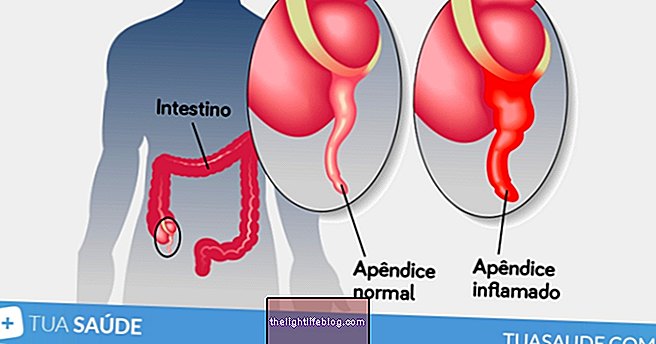
2. Intestinal infection
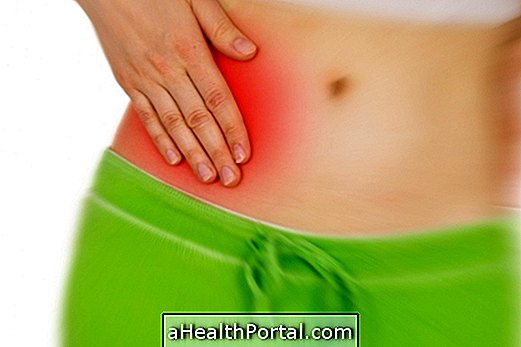
Having a bowel infection causes symptoms like abdominal pain and diarrhea, and it is common for feces to appear yellowish because the gut did not have time to absorb the fat from the food. The main cause of this problem is E. coli bacteria, so check out its symptoms here.
What to do: Drink plenty of water and consume easily digestible foods such as cooked or baked fruits, cooked white rice, fish and white meats, avoiding red meat and processed foods.

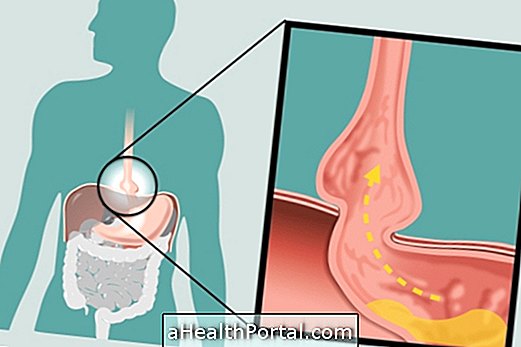
3. Liver or Gallbladder Problems
Diseases such as hepatitis, cirrhosis or stone in the gallbladder cause less bile to reach the intestine, which is the substance responsible for helping in the digestion of fats. In addition to changing the color of feces, these diseases also often cause symptoms of abdominal pain and yellowing of the skin and eyes.
What to do: In the presence of these symptoms, one should seek the doctor to confirm the diagnosis and initiate the appropriate treatment.
4. Pancreas Problems
Changes in the pancreas cause poor digestion, making the stools whitish or yellowish, as well as causing them to float and look foaming. The main problems affecting this organ are pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, cystic fibrosis or obstruction of the pancreatic canal.
What to do: In the presence of these changes, especially if accompanied by abdominal pain, nausea and lack of apatite, one should seek the doctor to confirm the diagnosis and initiate the appropriate treatment.
5. Giardiasis
Giardiasis is an intestinal disease caused by the Giardia parasite and causes symptoms such as diarrhea with yellowish stools, nausea, headache, low fever and weight loss.
What to do: In the presence of these symptoms, one should seek the doctor and do stool tests to confirm the presence of the parasite in the intestine and initiate appropriate treatment, which is usually done with antibiotics.
6. Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is a severe intolerance to gluten that causes irritation and intestinal malabsorption when the patient consumes food with wheat, rye, or barley, which leads to increased fat in the stool.
What to do: It is important to seek the doctor to confirm the diagnosis of the disease and start a gluten-free diet. See all the symptoms of this disease here.
7. Use of medicines
The use of weight-loss medications that work by decreasing the absorption of fat in the intestine, such as Xenical and Biofit, also cause changes in stool color and increase intestinal transit.
What to do: If these medicines have not been recommended by your doctor, you should stop using them and schedule a medical consultation to get advice on the correct use of the medication.
What are feces made of?
Most feces are made up of water, and in lesser amounts are bacteria from the intestinal flora, liquids that help digest food, such as bile, and food remains that have not been digested or absorbed, such as fibers, grains, and seeds.
Thus, changes in diet, use of medications or the presence of some intestinal problem can cause poor digestion, causing the fat in the diet to not be absorbed, which changes the color of the stool to yellow.
Find out what causes each color change in the stool.









-e-como-tratar.jpg)