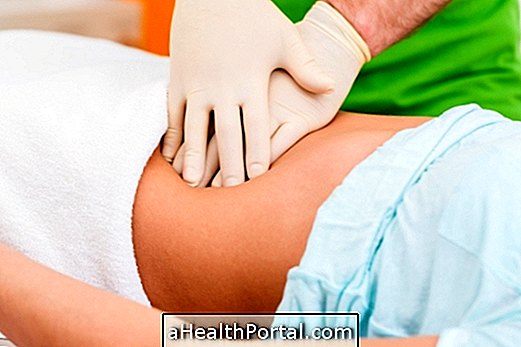
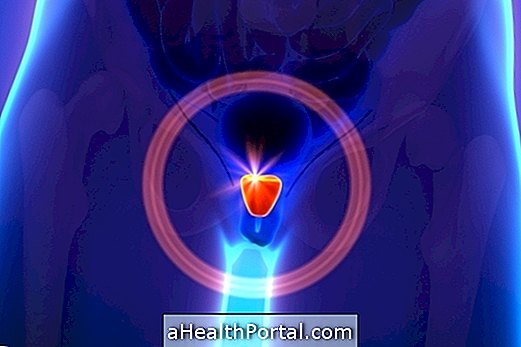
Rectal examination is an examination commonly known as performed by the urologist to look for possible changes in the prostate that may be indicative of prostate cancer or benign prostatic hyperplasia.
It is also an important test to evaluate changes in the rectum and anus by the coloproctologist, such as anal fissure, hemorrhoids or nodules. In addition, rectal examination can also be done on routine gynecological examination in women as it helps detect problems in the vaginal canal or uterus, for example.
The rectal examination is quick, performed in a doctor's office, does not interfere with sexuality and does not cause pain, but it can cause some discomfort if the person has anal fissures or a rectal infection. Understand what hemorrhoids are and how the treatment is done.
When to do
The rectal touch is most commonly performed by the urologist to track changes in the prostate, such as enlargement, common in benign prostatic hyperplasia, and to aid in the early diagnosis of prostate cancer, increasing the chances of cure. See which are the 10 signs that can indicate prostate cancer.
Thus in these cases, rectal examination is especially indicated for men aged 50 and older with or without signs and symptoms of organ changes, and in men aged 45 and older who have a history of prostate cancer in their family before age 60 .
In addition to investigating changes in the prostate, rectal examination may be done as part of the proctologist's proctology examination to:
- Identify lesions in the rectum and anus, such as ulcers, nodules, or tumors;
- Observe an anal fissure;
- Evaluate hemorrhoids;
- Look for causes of bleeding in the stool. Learn about the major causes of blood in the stool;
- Search for causes of abdominal or pelvic pain;
- Investigate the cause of an intestinal obstruction. Understand what can cause bowel obstruction and what the risks are;
- Detecting inflammations or abscesses in the final portion of the intestine. Check what a proctitis is and what it may cause;
- Look for reasons for intestinal constipation or fecal incontinence.
In the case of the female rectal examination performed during a routine gynecological examination, this examination can be performed because it is possible to palpate the posterior wall of the vagina and uterus, and may detect nodules and other abnormalities in these organs. Find out the top 7 exams recommended by the gynecologist.
Is there any preparation for the exam?
The rectal examination does not require any preparation to be done.
How is done
The rectal touch is done by inserting the index finger, protected by a latex glove and lubricated, in the patient's anus, allowing the patient to feel the anus and sphincter of the anus, the mucosa of the rectum and the end part of the intestine, and can also palpate the region of the prostate, in the case of men, and of the vagina and uterus, in the case of women.
Most of the time, the examination is performed in the lying position on the left side, which is the most comfortable position for the patient. It can also be performed in the geno-pectoral position, with the knees and chest supported on the stretcher, or in the gynecological position.
When the objective of the test is to evaluate the prostate, the doctor evaluates the size, density and shape of the prostate by touching, as well as checking the presence of nodules and other abnormalities in this organ. Rectal rash can also be done along with the dosage of PSA, which is an enzyme produced by the prostate that, when it has increased blood levels, may indicate some abnormality. Here's how to understand the result of the PSA exam.
Although they are two very effective tests to aid in the diagnosis of prostate cancer, if they are altered they can not complete the diagnosis, which is done only through biopsy. In addition, the rectal touch only allows palpation of the posterior and lateral portions of the prostate, and the organ is not evaluated completely. Find out the 6 exams that evaluate the prostate.