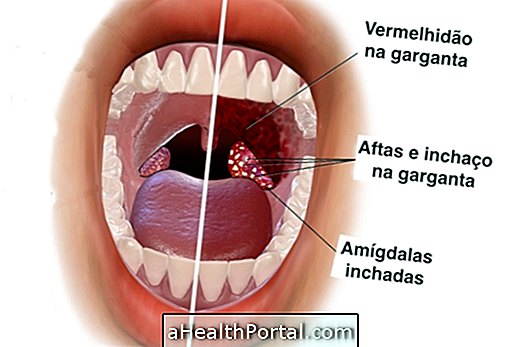
Sexually transmitted diseases, such as gonorrhea or AIDS, can occur when having sex without a condom, either through intimate vaginal, anal or oral contact. However, the chances of infection increase when you have several partners in the same time period, and these diseases also affect men and women of all ages.
Generally, these infections cause symptoms that affect the genitals such as pain, redness, small wounds, discharge, swelling, difficulty urinating or pain during intimate contact, and to identify the correct disease, it is necessary to go to the gynecologist or urologist to make specific tests.
For treatment, the doctor usually indicates the use of antibiotics or antifungals in the form of tablets or ointments, since most STDs have a cure, with the exception of AIDS and herpes. The following are the symptoms and treatment forms of all STDs, also called sexually transmitted infections and venereal diseases.
1. Chlamydia

Chlamydia can cause symptoms such as yellowing and thick discharge, redness in the genitals, pain in the pelvis and during intimate contact, but in many cases the disease does not cause symptoms and the infection goes unnoticed.
The disease, which is caused by a bacterium, can be caused by unprotected intimate contact or by sharing sex toys, for example.
How to treat: Usually, the treatment is done with antibiotics like Azithromycin or Doxycycline. Learn more about Chlamydia.
2. Gonorrhea

Gonorrhea is a disease caused by bacteria, also known as warming, which can occur in men and women and is transmitted by unprotected intimate contact or by sharing sex toys.
The bacteria can cause pain when urinating, pus-like yellow discharge, vaginal bleeding outside of menstruation, abdominal pain, red lips in the mouth or pain during intimate contact, for example.
How to treat: Treatment should be done with the use of Ceftriaxone and Azithromycin and, if not done, may affect the joints and blood and may be life-threatening. See other treatments that can strengthen the immune system with Echinacea tea and help treat the infection.
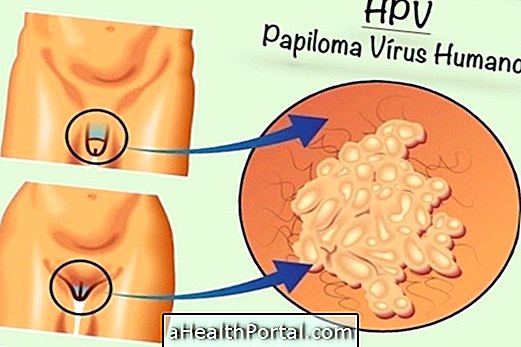
3. HPV - Genital warts

This infection is caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), which leads to the growth of lesions on the skin of the genitals of men or women that may have soft or rough texture, color that varies with skin tone and do not cause pain but are contagious diseases.
How to treat: Genital warts have no cure because the HPV virus remains dormant in the body, but there is treatment with the application of ointments such as Aldara or Wartec on warts. Seizures can arise due to excessive alcohol consumption, high fatigue and stress, for example.
Learn how to do seat baths to complement the treatment for genital warts.
4. Genital Herpes

Genital herpes is an easily transmitted disease caused by the cold sore virus and causes small red marbles on the skin very close to each other, containing a virus-rich, yellowish-colored liquid with redness around it that causes itching, affecting mainly the thighs, anus and genitals. In addition, they can cause fever and pain when urinating and discharge in the case of the woman. Learn all the symptoms that genital herpes can cause.
How to treat: Treatment should be done with medicines such as Acyclovir, Valacyclovir or Famciclovir, helping to reduce the discomfort caused by the symptoms, as the infection has no cure and symptoms can take up to 20 days to disappear. Get to know other natural strategies to complement the treatment for genital herpes.
5. Trichomoniasis

Trichomoniasis is caused by a parasite that causes symptoms such as greyish or yellowish-green discharge and frothy with strong and unpleasant bad odor, and may cause redness, intense itching and swelling of the genitals. Learn how to distinguish the symptoms of trichomoniasis in men and women.
Infection is uncommon and can also be spread by sharing wet towels, bathing or using a jacuzzi and treatment is done by taking Metronidazole.
How to treat: usually the treatment of this infection is done with the use of antibiotics, like Metronidazole or Tioconazol, for 5 to 7 days. If treatment is not done, there is a greater chance of developing other infections, having a preterm birth or developing prostatitis.
6. Syphilis

Syphilis is a disease that causes wounds and red spots on hands and feet that do not bleed or cause pain, and can cause blindness, paralysis and heart problems, and transmission is by transfusion of contaminated blood and by sharing syringes or needles and, the first symptoms appear 3 and 12 weeks after the contagion. See more syphilis symptoms.
How to treat: The treatment is done with medicines like Penicillin G or erythromycin and when done correctly there are chances of cure.
7. AIDS

AIDS causes symptoms such as fever, sweating, headache, sensitivity to light, sore throat, vomiting and diarrhea and the disease has no cure, only treatment to decrease symptoms and increase time and quality of life.
How to treat: Treatment is done with antiretroviral drugs, such as Zidovudine or Lamivudine, for example, which are provided free of charge by SUS. These drugs fight the virus and strengthen the immune system, but do not cure the disease.
Learn all about this disease in the video:

How do I know if I have an STD?
The diagnosis of a sexually transmitted disease can be made based on the symptoms and observation of the genitals, being confirmed through examinations, such as the pap smear and the Schiller test, for example.
In addition, your doctor may order a blood test to check the cause of the disease and indicate the most appropriate treatment.
When to repeat the exams
When a woman or man has acquired a sexually transmitted disease, the doctor recommends having a physical examination at least every 6 months for about 2 years, until the result of 3 consecutive tests is negative.
During the treatment phase it may be necessary to go to the doctor several times a month to adjust the treatment and cure the disease, if at all possible.
Forms of STD infection
STDs, in addition to being transmitted through unprotected sexual contact, may be transmitted:
- From mother to child through blood during pregnancy, through breastfeeding or during childbirth;
- Syringe sharing;
- Sharing of personal objects, such as towels;
In some cases, very rare, the development of the disease can occur through blood transfusion.
How not to get an STD?
The best way to avoid getting contaminated is by using condoms in all relationships, in intimate vaginal, anal and oral contact, as contact with secretions or with the skin can transmit the disease. However, it is crucial to put condoms properly before any contact. Know how:
- Put on the male condom properly;
- Use the female condom.
What can happen if treatment is not done?
When STDs are not treated correctly, more serious problems such as cancer of the uterus, infertility, heart problems, meningitis, abortion, or malformations of the fetus may arise.
Check out a great home remedy that helps to complement the treatment here.