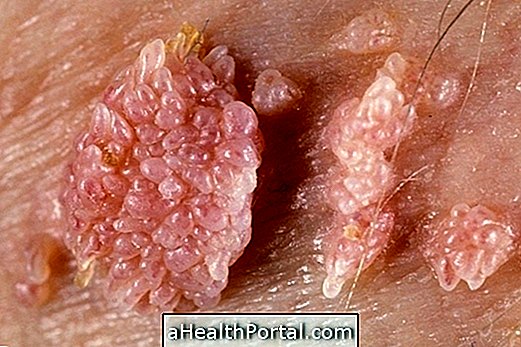
Cauterization of the cervix is a treatment used in cases of wounds in the uterus caused by HPV, hormonal changes or vaginal infections, for example, as well as in cases of excessive bleeding or discharge after intimate contact. See the main causes of wounds in the womb: Wound in uterus.
Generally, during cauterization of the cervix, the gynecologist uses a device to burn lesions in the cervix, allowing healthy new cells to develop in the affected site.
Cauterization of the uterine cervix can be done at the gynecologist's office with local anesthesia and therefore does not hurt, but some women may experience some discomfort at the time of the doctor's cauterization.
How cauterization is done
Cauterization of the cervix is done in a manner similar to the pap smear, so the woman should remove the clothing below the waist and lie on the gynecologist's stretcher with her legs slightly apart to allow the introduction of an object that maintains the open vaginal canal and which is called a speculum.
Then the gynecologist puts anesthesia in the cervix to prevent the woman from feeling pain during the procedure and inserts a longer device to burn the lesions of the cervix, which can take between 10 and 15 minutes.
How is recovery after cauterization
After the cauterization, the woman can return home without being hospitalized, however, should not drive due to the effects of anesthesia, and it is therefore recommended that it be accompanied by a relative.
In addition, during recovery of cauterization of the cervix, it is important to know that:
- Abdominal cramps may occur within the first 2 hours after the procedure;
- Small bleeding may occur up to 6 weeks after cauterization;
- Avoid close contact or use tampons until bleeding subsides;
In cases where a woman has many abdominal cramps after cauterization, her doctor may prescribe analgesics, such as Paracetamol or Ibuprofen, to help relieve pain.
When to go to the doctor
It is recommended to go to the emergency room when:
- Fever above 30th;
- Foul-smelling discharge;
- Increased bleeding;
- Excessive tiredness;
- Redness in the genital area.
These symptoms may indicate the development of an infection or bleeding and therefore one should go to the hospital immediately to initiate appropriate treatment and avoid the development of serious complications.