Infantile intestinal infection is a very common childhood disease that occurs when the body reacts against the entry of viruses, bacteria, parasites or fungi into the gastrointestinal tract and can cause symptoms such as diarrhea, vomiting, nausea and fever in the child.
The treatment of this infection is done with rest, adequate diet and the ingestion of liquids, including water, milk, coconut water or homemade serum every 15 minutes, to avoid dehydration. In cases of intestinal bacterial infection infantile, and in special cases, the treatment can also be done with antibiotics, always prescribed by the pediatrician:
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Ceftriaxone;
- Cotrimoxazole.
Remedies for diarrhea or nausea are not indicated because diarrhea is a bowel defense reaction that is attempting to eliminate the offending agent and in addition, the child tends to vomit the remedies, and in suppositories, the intestine can not absorb them. Analgesic drugs, such as Ibuprofen or Paracetamol, for example, should only be used only in cases of fever and pain in the body and always under the guidance of the pediatrician.
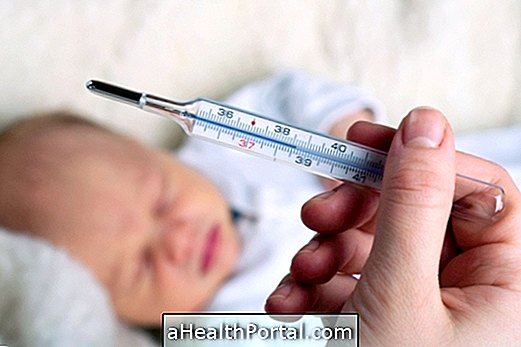
Typically, fever and motion sickness disappear within the first 2 to 3 days, but the child's recovery varies from 4 to 5 days, up to a week or more. However, if the infant intestinal infection is not treated, the child may become dehydrated and develop other complications such as intestinal mucosal lesions, metabolic loss or malnutrition.
Diet for infantile intestinal infection
The diet for infantile intestinal infection should include:
- Prepared foods in the form of purees, cooked or roasted;
- Soups or chicken soup with little oil and seasonings;
- Crackers of water and salt, maria or corn;
- Natural sucrose;
- Peeled fruits or vegetables.
It is important to avoid frying, whole-grain breads, cereals, bran, industrialized snacks, pastries, filled biscuits, chocolate, soft drinks and cow's milk.
Symptoms of intestinal infection in the baby
Symptoms of infection of the infant gut as well as the symptoms of intestinal infection in baby include:
- Diarrhea;
- Intense abdominal pain that makes the child cry;
- Fever;
- Vomiting;
- I get sick.
Infantile intestinal infection with blood occurs in the most severe cases of intestinal infection caused by bacteria, also known as dysentery, which can provoke the escape of blood and mucus in the stool.
What Causes Infection
Intestinal infection in a baby is usually caused by viruses, through contact with contaminated saliva or feces, during diaper changes or in contact with a sick child's toys.
However, intestinal infection in a baby can also be caused by bacteria, through contact or consumption of contaminated water, juices, ingestion of spoiled foods, fruits and vegetables that have been in places with infected animals. Thus, it is very important to give the baby only boiled or filtered water and to adopt good hygiene care, including in the preparation of food.