Symptoms of urinary tract infection, such as pain or burning on urination, may vary from person to person as the infection can affect the urethra, bladder, or kidneys.
If you think you may have a urinary tract infection, select what you are feeling and see the risk of having an infection:
- 1. Pain or burning sensation when urinating Yes No
- 2. Frequent and sudden urge to urinate in small amounts Yes No
- 3. Feeling of not being able to empty the bladder Yes No
- 4. Feeling of weight or discomfort in the bladder area Yes No
- 5. Dark or bloody urine Yes No
- 6. Persistent low fever (between 37.5º and 38º) Yes No
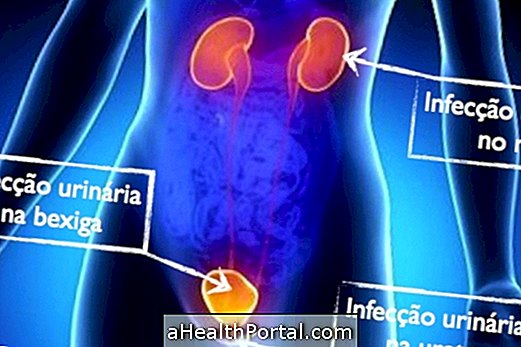
Generally, urinary tract infection is caused by bacteria from the gut that enter the urinary system and is therefore more frequent in women because of the proximity of the anus to the urethra.
Treatment for urinary tract infection should be guided by a urologist and usually includes taking antibiotics, such as Ceftriaxone, because when it is not properly treated, it can spread throughout the body, putting your life at risk.
1. Urethritis: infection in the urethra
Urethritis arises when bacteria infests the urethra, causing inflammation and symptoms such as:
- Frequent urge to urinate;
- Difficulty starting urination;
- Pain or burning to urinate;
- Yellowish discharge in the urethra.
In these cases it is advisable to consult a urologist to start treatment with antibiotics, in order to eliminate the bacteria from the urethra. However, you should also keep the intimate region clean and dry as well as increase your water intake.
See also a home remedy to help eliminate the symptoms faster.

2. Cystitis: bladder infection
Bladder infection is the most common form of urinary tract infection and occurs when bacteria can pass through the urethra and reach the bladder, causing:
- Urgent urge to urinate, but in a small amount;
- Burning sensation when urinating;
- Presence of blood in the urine;
- Urine blurred with intense and unpleasant smell;
- Abdominal pain or feeling of heaviness in the belly;
- Fever of 37.5 to 38 ° C.
It is recommended to consult a urologist as soon as one or more of these symptoms appear to initiate appropriate antibiotic treatment to prevent the infection from spreading to the kidneys.
In case of back pain, fever above 38 ° C or vomiting should go immediately to the emergency room.
Learn more about how this issue is handled.
3. Pyelonephritis: Kidney infection
Most urinary tract infections affect only the urethra or bladder, but in the most severe cases, bacteria can reach the kidneys and cause a more serious infection, leading to:
- Fever above 38.5 ° C;
- Severe pain in the belly, back or groin;
- Pain or burning while urinating;
- Urine blurred;
- Presence of pus or blood in the urine;
- Frequent urge to urinate.
In addition, chills, nausea, vomiting, and excessive tiredness may also occur. In the elderly, this type of infection usually causes confusion even before the other symptoms appear.
In the case of suspected pyelonephritis, it is important to go to the hospital immediately to identify the problem and initiate antibiotic treatment directly into the vein.
If you think you may have a urinary tract infection, here's what you can do:

Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infection in Baby
Identifying the symptoms of urinary tract infection in the baby can be difficult as babies and children can not explain what they are feeling. However, in these cases the most common signs are:
- Fever above 37.5 ° C for no apparent reason;
- I cry when I urinate;
- Urine with intense odor;
- Presence of blood in the diaper;
- Constant irritability;
- Decreased appetite.
Whenever these symptoms appear, it is important to consult your pediatrician to assess the possibility that the baby is developing a urinary tract infection. Understand how treatment is done in these cases.
Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infection in Pregnancy
The symptoms of urinary tract infection in pregnancy are the same as when you are not pregnant. But during gestation, the infection is more common, due to the low immune system and the increase of proteins in the urine that cause greater growth and development of bacteria.
Treatment for urinary tract infection during pregnancy can be done with the ingestion of antibiotics that do not affect pregnancy and which include Cefaclor, Cefadroxil and Cephalotin. Learn more about the remedies used to treat urinary tract infection in pregnancy.