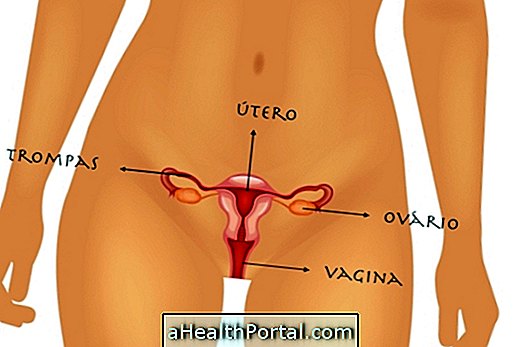
Sacrocyteitis is an inflammation in the joint of the sacrum with the hip that generates pain and discomfort at the end of the spine. Their treatment is basically done with the taking of analgesic remedies, anti-inflammatory, muscle relaxants and physiotherapy sessions.
In spite of the treatment it is common to have several recurrences of the disease during the life because besides a pre-genetic disposition for such, often there is a difference in the articulation of the hip, that generally is aggravated by the difference of length of the legs, when one is a few centimeters bigger than the other. This change leads to compensation throughout the body structure, including in the articulations of the spine, leading to the persistence of sacroiliitis.
Symptoms of sacroiliitis
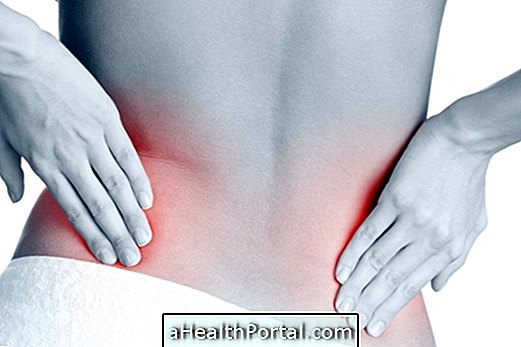
Symptoms of sacroiliitis include:
- Pain in the joints of the sacrum with the spine. The pain is deep and located in the upper part of the buttock, and can radiate to the thigh;
- Sometimes there is pain in the lower back or hip;
- Pain is frequent, and is present even during sleep;
- Pain may worsen after prolonged rest, being more intense upon waking;
- Pain or discomfort in the knees;
- Contractures in the lower back and near the sacroiliac joint;
- There may be a fever when it is caused by an infection.
The diagnosis is made by the physician after the observation of clinical signs when pressing the iliac crest, and of imaging tests, such as x-ray and scintigraphy, for example.
Treatment for Sacroiliitis
When identifying the symptoms of sacroiliitis, the physician should advise the patient to do physical therapy to reduce pain and discomfort. Strengthening and stretching exercises will be able to improve posture and decrease the symptomatology of the disease. Check out 5 exercises indicated for sacroiliitis here.
Taking anti-inflammatory and analgesic medications and physiotherapy sessions are ways to find relief from the symptoms and decrease the crisis.
Postural reeducation and osteopathy are also some forms of treatment that help decrease the compensations and pain, bringing relief of the symptoms and therefore are also indicated.
If there is a difference in leg size greater than 1 centimeter, it is recommended to use an insole continuously to adjust the height of the limb and decrease the overload at the joint.
When the cause of the sacroiliitis is the presence of microorganisms, the treatment is done with the use of antibiotics during hospitalization.
What causes sacroiliitis
Some causes of sacroiliitis include:
- Have one leg bigger than the other, even if the difference is only 0.5 cm;
- Neck ridges such as arthrosis, hyperescoliosis, hyperciphosis, hyperlordosis or parrot's beaks;
- Misaligned temporomandibular joint (TMJ);
- Malignant or benign tumor that compresses the sacroiliac joint;
- Direct trauma, like a blow, for example;
- Repetitive trauma, as occurs in the case of high competition jumpers, for example;
- Indirect trauma, as in an automobile accident, for example;
- Calcification of the sacroiliac;
- Dislocation of the hip joint;
- Diseases such as sarcoidosis, Paget's disease, osteomalacia, acromegaly, tuberculosis;
- Infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus, other bacteria are described less frequently, such as Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus, Salmonella, Pseudomonas, Klebisiela and N. gonorhea.
Individuals diagnosed with this disease should be aware as they are more likely to develop ankylosing spondylitis in the future, which is a severe degenerative disease.