Cytomegalovirus, also known as CMV, is a virus in the same herpes family, which can cause symptoms such as fever, sore throat, and swollen belly. Like herpes, this virus is also present in most people, but only causes symptoms when the immune system is weakened, such as in pregnant women, people with HIV, or in patients taking cancer treatment, for example.
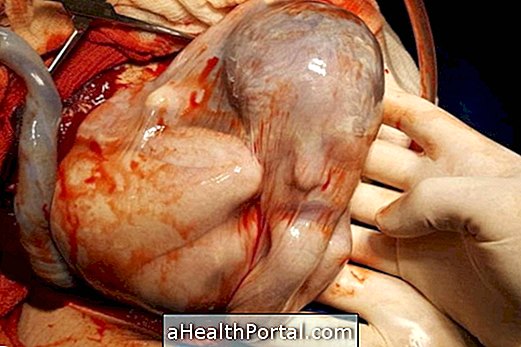
During pregnancy, this virus is detected through prenatal testing, but is usually harmless and causes no change in the baby, especially when the woman was infected before she became pregnant. However, when a woman is infected during pregnancy, the virus can cause problems like microcephaly and deafness in the baby.

Main symptoms
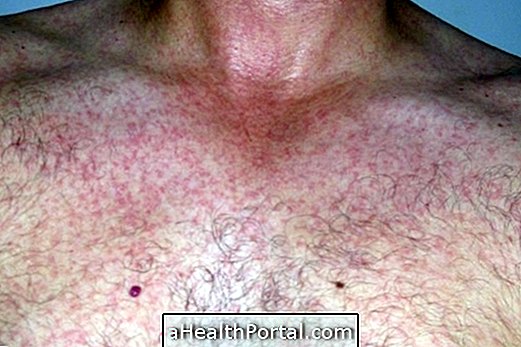
When the virus affects a new person there are no symptoms that show their presence in the body, so it is common for the patient to only find out that he is infected when he does a specific blood test for the virus.
However, some symptoms may arise when the immune system is low:
- Fever above 38ºC;
- Sore throat;
- Excessive tiredness;
- Swelling of the belly;
- Sore belly
Due to the risk of causing malformations in the baby all pregnant women should be tested for the virus even without the symptoms so as to start treatment if necessary to prevent the virus from affecting the baby.
Understand what happens when the baby is infected with cytomegalovirus.
How to diagnose
The diagnosis of cytomegalovirus infection is made through specific blood tests, which show if there are antibodies against the virus. When the result of the test results in the CMV IgM reagent result, it indicates that the virus infection is still at the beginning, but if the result is CMV IgG reagent, it means that the virus is present in the body for a longer time, life, just as with herpes.
In pregnancy, if the result is CMV IgM reagent the pregnant woman should start treatment with antivirals or immunoglobulins to avoid transmission to the baby. See how treatment is done in these cases.
How is the treatment done?
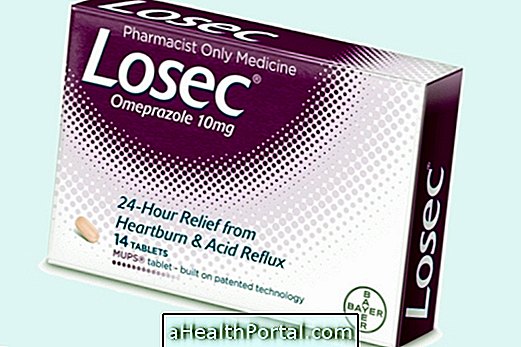
There is no medicine capable of eliminating the virus from the body and so the treatment is done with painkillers, such as Paracetamol, to relieve symptoms such as headaches and fever.
This treatment usually lasts about 14 days and can be done at home using the remedies prescribed by the doctor, rest and adequate water intake.
However, in special cases, such as during pregnancy or when the infection is highly developed, the doctor may prescribe the use of antivirals to reduce the burden of the virus in the body, but it can not be completely eliminated.

Main complications
Complications of cytomegalovirus occur mainly in children who are infected with the virus during pregnancy, and include:
- Mental retardation;
- Delayed development;
- Convulsions;
- Cerebral palsy;
- Defects in tooth formation;
- Paralysis of some parts of the body, especially of the legs;
- Deafness.
In adults, complications arise when the infection develops a lot, as in people with weakened immune systems, resulting mainly in blindness and loss of leg movements, for example.
How virus transmission occurs
Transmission of the cytomegalovirus can occur through contact with body secretions, such as cough and saliva, through intimate contact with an infected person or through the sharing of contaminated objects such as cups, cutlery, and towels.
In addition, the virus can also be transmitted through blood transfusions or from mother to child, especially when the pregnant woman is infected during pregnancy.