Pulpitis is an inflammation of the dental pulp, a tissue with several nerves and blood vessels located inside the teeth.
The main symptom of pulpitis is toothache, due to inflammation and infection of the dental pulp, which can be very intense, and which usually worsens in the presence of stimuli, such as chewing or eating hot or cold drinks and foods.
Depending on the degree of inflammation, pulpitis can be:
- Reversible: when the nerves and vessels, although inflamed, are not destroyed, they can improve with the removal of causes and stimuli, such as cavities;
- Irreversible: the nerves and vessels of the pulp are necrotic and destroyed by inflammation and infection, so the dental pulp must be completely removed and replaced with a filling of the affected tooth canal.
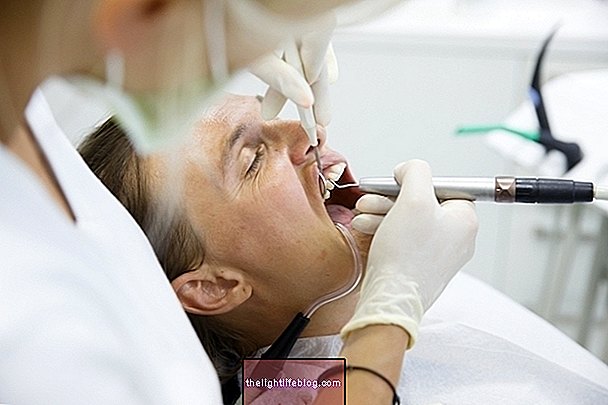
The diagnosis of the type of pulpitis is made by the dentist through assessments with temperature or electrical stimuli, therefore, in the presence of toothache, it is necessary to go to an appointment so that confirmation and treatment are done soon and complications are avoided, like a dental abscess.

Main causes
Some of the most common causes of pulpitis are:
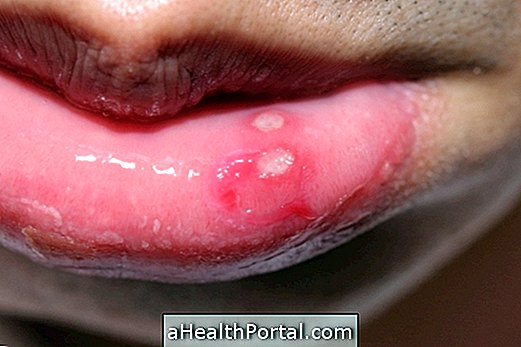
- Caries: are the main cause of pulpitis and are characterized by infection by bacteria that destroy tooth tissues, reaching even the deepest parts and reaching the pulp. See how to identify and treat tooth decay;
- Knock on the tooth, due to falls or accidents, for example;
- Bruxism, which is the unconscious act of clenching or grinding your teeth, especially during sleep, which causes wear and trauma to the tooth;
- Incorrect chewing, which causes minor trauma to the jaw and teeth;
- Periodontitis, when it is not treated and becomes advanced to the point of reaching the root of the tooth;
- Chemotherapy or radiotherapy, which can also stimulate lesions in the tissues of the teeth;
- Aggressions by chemical products, such as acids, or sudden changes in temperature.
These situations cause aggression and inflammation of the nerve roots and blood vessels that form the pulp of the tooth, being responsible for pulpitis.
How the treatment is done
To treat pulpitis, it is important to know its cause and whether it is a reversible or irreversible condition, which is determined by the dentist.
Reversible pulpitis is usually detected in cases of more initial inflammation, and is treated by removing the irritant condition. Thus, if it is caused by a cavity, for example, the solution may be the restoration of the tooth, or, in cases of blow, the performance of rest and use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
In order to treat irreversible pulpitis, a procedure called endodontics, pulpectomy or devitalization of the tooth is performed, which is characterized by the removal of pulp from the tooth, and replacement by filling, through a root canal. In the latter case, when none of the previous alternatives is sufficient, tooth extraction, also called tooth extraction, can be performed.
In addition, when the pulpitis is purulent or shows signs of infection, the dentist will guide the use of an antibiotic, such as Amoxicillin or Ampicillin, for example, and may also prescribe pain relief medications, such as a pain reliever or anti-inflammatory. like Dipyrone or Ibuprofen.
Home remedy for pulpitis
Some natural tips can be followed at home to help relieve the pain caused by pulpitis, but without ever replacing the treatment guided by the dentist. A great option is to drink mint tea, which has soothing and refreshing properties that will help to control toothache better.
Mouthwashing with apple and propolis tea is also recommended, as it has inflammatory, analgesic and antiseptic properties. Other options are chewing a clove or mouthwash with water and salt.
Check out these and other recipes on home remedies for toothache.

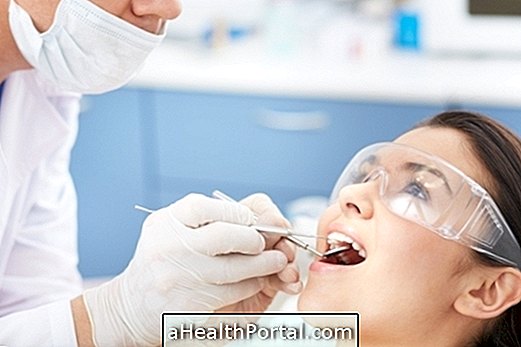
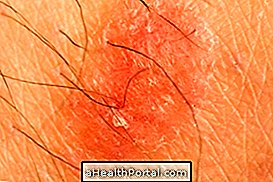
Caries causing inflammation of the pulp of the tooth
Main types of pulpitis
Pulpitis is considered acute when the injury occurs in a short period of time, usually between 2 to 14 days, with sudden and intense symptoms. Inflammation produces secretions, which vary depending on the type:
- Serous pulpitis, with secretion without pus, less severe;
- Suppurative or purulent pulpitis, due to the presence of infection, which causes the accumulation of pus, and causes inflammation and intense symptoms.
Acute pulpitis is usually reversible, however, if not treated quickly, it can become irreversible.
In chronic pulpitis, the inflammation occurs slowly, slowly, and with a longer tooth degeneration. It can be divided into:
- Chronic ulcerative pulpitis, when the tooth wears to the point of exposing the pulp, which causes bleeding;
- Chronic hyperplastic pulpitis, when the pulp of the tooth proliferates due to inflammation, forming a kind of polyp, and causes a feeling of pressure on the tooth.
- Chronic sclerosing pulpitis, is a degeneration that happens gradually due to age, being common in the elderly.
Chronic pulpitis does not cause as many symptoms as acute pulpitis, and is often asymptomatic and more difficult to detect. Due to the intense degradation of the pulp of the tooth, these types of pulpitis are usually irreversible.
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther
-para-que-serve-e-como--feito.jpg)









.jpg)