Viral meningitis is an inflammation of the membranes lining the brain and spinal cord due to the entry of a virus into this region. The symptoms of meningitis manifest initially with a high fever and intense headache.
After a few hours the irritation of the meninges to the pain report is noticed when the person tries to put the chin in the chest. Numbness and refusal to feed occur soon after. Increased pressure within the skull causes symptoms such as changes in consciousness, severe headache, vomiting, and difficulty with clarity.
Thus, the symptoms of viral meningitis are usually:

- High fever;
- Severe headache;
- Nuchal rigidity manifested through difficulty in moving the neck and touching the chin in the chest;
- Difficulty in lifting the leg while lying on the stomach;
- Nauseation and vomiting;
- Intolerance to light and noise;
- Tremors;
- Hallucinations;
- Somnolence;
- Convulsions.
Drowsiness, irritability, and easy crying may occur in children less than 2 years of age.
In addition, in some people Waterhouse-Friederischsen syndrome, which is a version of extremely serious viral meningitis caused by Neisseria meningitis, can develop. In this case there are symptoms such as very severe diarrhea, vomiting, convulsions, internal bleeding, very low pressure and the person can go into shock and there is a risk of death.
How to Confirm Viral Meningitis
The person who presents 3 symptoms like these should be considered with suspected meningitis and one should start using antibiotics. However, if you get bought through tests that are not a bacterial meningitis, these medications are not necessary.
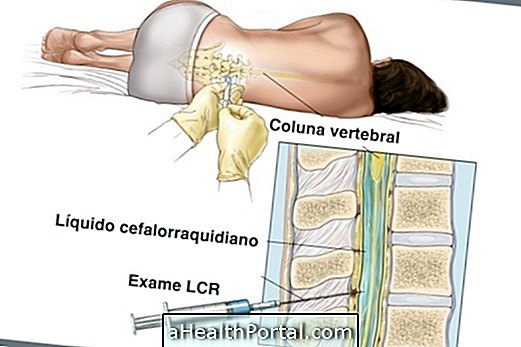
The diagnosis of viral meningitis is made through examination of blood, urine, faeces and also lumbar puncture, which removes a sample of the cerebrospinal fluid that covers the whole nervous system. This test can identify the disease and its causative agent. After identifying the disease it is also important to know in which phase of severity the person is. There are 3 phases of severity:
- Stage 1: When the person presents mild symptoms and does not have alterations of the conscience;
- Stage 2: When the person presents drowsiness, irritability, delirium, hallucinations, mental confusion, personality alteration;
- Stage 3: When the person is apathetic or falls into a coma.
People diagnosed with viral meningitis in stages 1 and 2 have a better chance of recovery than those in stage 3.
Treatment for Viral Meningitis
After the diagnosis of the disease, it is necessary to start the treatment that is done by taking medications to lower the fever and relieve other discomforts. Taking antibiotics is only effective in cases of meningitis caused by bacteria, and therefore, for the most part, they are not indicated in this situation.
Most of the time the treatment is done in the hospital, but in some cases the doctor can let the person perform the treatment at home. As viral meningitis has a better recovery than in case of bacterial meningitis, hospital admission is advised only to keep the person well hydrated, even after vomiting and diarrhea.
Recovery usually occurs within 1 or 2 weeks but the person may become weak and feel dizzy for weeks or even months after the end of treatment. Sometimes the person may have some sequelae such as loss of memory, smell, difficulty swallowing, personality change, imbalance, seizures and psychosis.
Get to know 5 practical steps to protect yourself from viral meningitis in your day-to-day life.