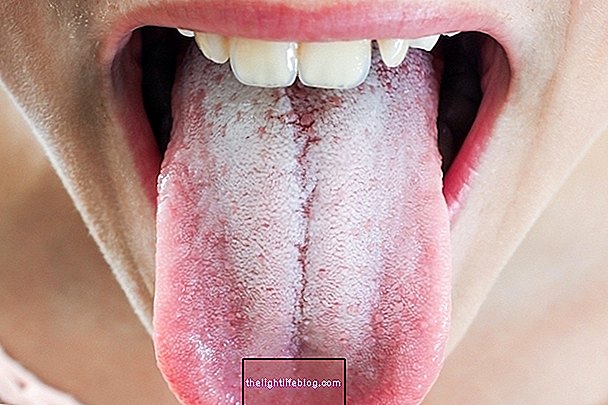
The white tongue is usually a sign of excessive growth of bacteria and fungi, which causes dirt and dead skin cells to become trapped between the inflamed papillae, creating white plaques.
Thus, white tongue is more common when there are favorable conditions for fungal growth, such as in people who do not have adequate oral hygiene or who have a weakened immune system, such as babies, the elderly or patients with autoimmune diseases, for example.
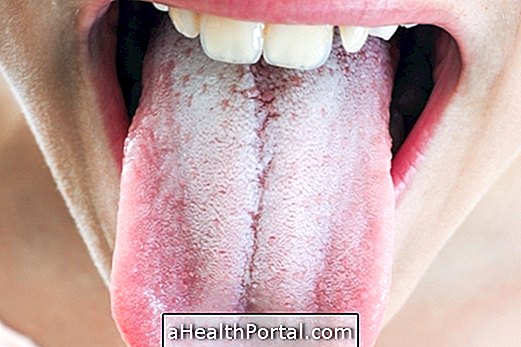
However, there are other diseases that can cause the appearance of white spots on the tongue, such as:
1. Flat lichen
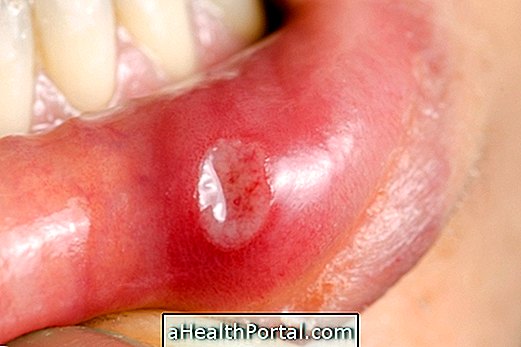
Lichen planus is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation of the lining of the mouth, which can lead to frequent white spots on the tongue and even inside the cheeks, as well as small painful canker sores. It is also common to feel burning in the mouth, as well as excessive sensitivity to hot, spicy or acidic food.
Understand better what oral lichen planus is and how the treatment is done.
- What to do : It is recommended to consult the general practitioner, as there is no remedy capable of curing lichen planus; however, your doctor may prescribe the use of corticoid medicines, such as Triamcinolone, to relieve inflammation and pain. In addition, using toothpaste without sodium lauryl sulfate may also help prevent the onset of symptoms.
2. Leukoplakia
This is a chronic disease that causes whitish plaques to appear on the inside of the cheeks, gums and, in some cases, on the surface of the tongue. This type of plaque does not improve with brushing of the tongue and is usually not painful.
Although there is no known cause for this change, it is more common in smokers and may be related to early signs of cancer of the mouth.
- What to do : If after 2 weeks of proper oral hygiene the plaques do not start to disappear it is important to consult a general practitioner or dentist to assess the risk of early signs of cancer. If they are benign plaques, your doctor may recommend the use of antivirals or have minor surgery to remove the plaques.

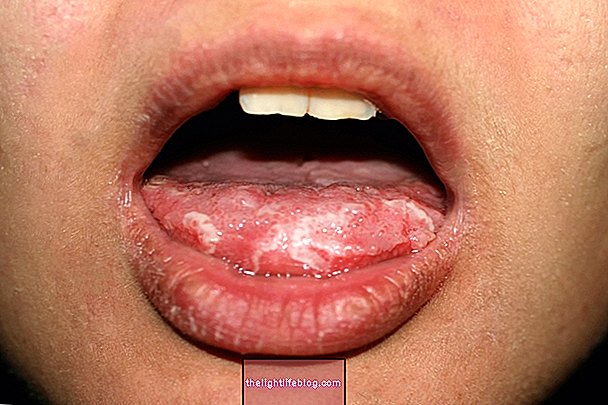
3. Oral Candidiasis
Oral candidiasis, also known as thrush, is the most common cause of white spots on the mouth, especially in bedridden or infants due to excessive fungal growth. However, it can also occur in adults who do not have proper mouth hygiene or who have autoimmune diseases, such as lupus or HIV.
This fungal infection can also be accompanied by bad breath, burning in the affected regions and the feeling of cotton inside the mouth. See how the treatment is done.
- What to do : Proper oral hygiene should be done by brushing the teeth at least 2 times a day and using a mouthwash to prevent the development of bacteria. In addition, if symptoms do not improve after 1 week, consult your GP to start using oral antifungal agents, such as Nystatin.
4. Syphilis
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease that can affect the mouth when having unprotected oral sex, and the first symptoms can take up to 3 months to appear. In these cases, sores in the mouth may also appear, characteristic of the first stage of the disease. Learn more about the symptoms and stages of syphilis.
- What to do : The treatment needs to be done with a penicillin injection, so a general practitioner should be consulted to make the diagnosis and start treatment. If treatment is not done, the symptoms may improve after 3 weeks, but the disease will progress to its second stage, in which it may spread to the rest of the body.
When to go to the doctor
In most cases this symptom is not a sign of a serious illness and can be easily treated with proper brushing of the tongue and frequent ingestion of water. However, if the white tongue lasts for more than 2 weeks or comes with pain or burning, for example, it is advisable to consult a general practitioner to assess if there is any disease and to initiate appropriate treatment if necessary.