Gonorrhea is a Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which is transmitted from person to person through anal, oral or penetrative intercourse. In most cases, gonorrhea does not cause symptoms, being discovered only after routine examinations, however in some people there may be pain or burning when urinating and a yellowish-white discharge, similar to pus.
It is important that gonorrhea is identified and treated quickly with antibiotics indicated by the doctor, because otherwise, there is a risk of the person developing complications, such as infertility and pelvic inflammatory disease, for example.
Gonorrhea is curable when treatment is done according to the doctor's recommendation. However, some people may not respond correctly to the treatment due to the resistance acquired by the bacteria to the antibiotics commonly used, which makes healing difficult. In this case, it may be necessary to use a combination of different antibiotics to cure gonorrhea.
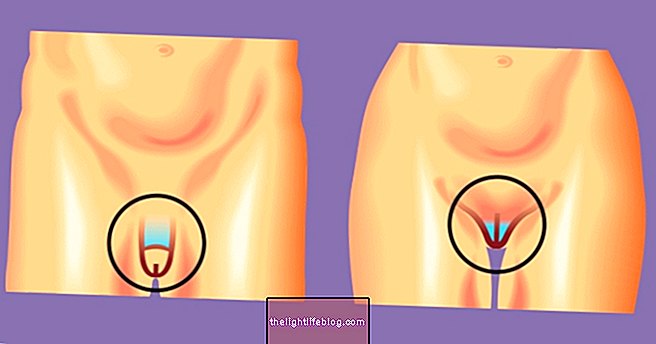
Gonorrhea symptoms
Symptoms of gonorrhea may appear up to 10 days after contact with the bacteria responsible for the disease, however, in most cases in women, gonorrhea is asymptomatic, being identified only at the time of routine gynecological examinations. In the case of men, most cases are symptomatic and the symptoms appear a few days after unprotected sexual contact.
In addition, the signs and symptoms of infection by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae may vary according to the type of unprotected sexual intercourse, that is, whether it was oral, anal or penetrative, with the most frequent symptoms being observed:
- Pain or burning when urinating;
- Urinary incontinence;
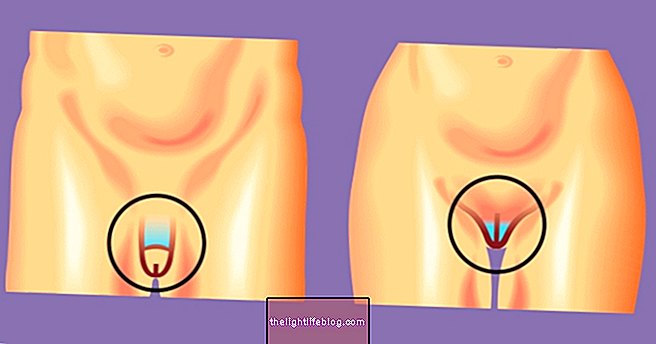
- Yellowish-white discharge, similar to pus;
- Inflammation of the Bartholin's glands, which are on the sides of the vagina and are responsible for the woman's lubrication;
- Acute urethritis, which is more common in men;
- Frequent desire to urinate;
- Sore throat and impaired voice when there is an oral intimate relationship;
- Inflammation of the anus, when there is an intimate anal intercourse.
In the case of women, when gonorrhea is not identified and treated correctly, there is an increased risk of developing pelvic inflammatory disease, ectopic pregnancy and sterility, and there is also an increased chance of the bacteria spreading through the bloodstream and leading to joint pain, fever and injury to the extremities of the body.
In men, the occurrence of complications is less frequent, because most of the time they are symptomatic, which makes the identification and start of treatment for gonorrhea faster and easier.
However, when treatment is not carried out in accordance with the urologist's guidance, complications such as urinary incontinence, a feeling of heaviness in the penis area and infertility can arise. Learn how to identify gonorrhea in men.
Gonorrhea in newborns
Gonorrhea in newborns can happen when the woman has the bacteria and the infection is not identified and treated during pregnancy, which increases the risk of transmitting the disease. Neisseria gonorrhoeae for the baby at the time of delivery.
Babies who come into contact with the bacteria during childbirth may have some signs and symptoms such as pain and swelling in the eyes, purulent discharge and difficulty opening the eyes, which can lead to blindness when not properly treated.
How the diagnosis is made
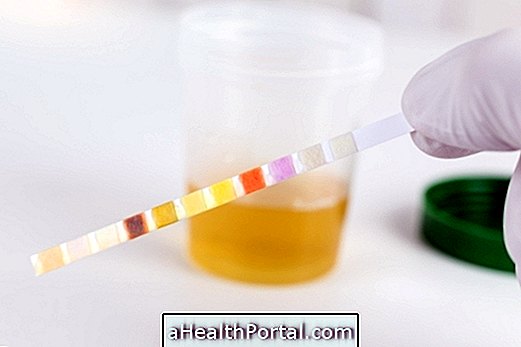
The diagnosis of gonorrhea is made by the gynecologist or urologist based on physical examinations and the result of laboratory tests, mainly microbiological, which are made based on the analysis of urine, vaginal or urethral secretion, in the case of men, which are collected in the laboratory. skilled.
The samples are taken to the laboratory for analysis where they are subjected to a series of tests to identify the bacterium, in addition to serological and molecular tests to identify the bacterium. Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
In addition, the antibiogram is performed in order to verify the sensitivity and resistance profile of the microorganism to the antibiotics normally used. That way, the doctor will be able to indicate the best antibiotic for the treatment of the person.
Gonorrhea treatment
Treatment for gonorrhea should be guided by a gynecologist, in the case of women, or a urologist, in the case of men, and is usually done with the use of Azithromycin tablets and Ceftriaxone in a single injection to eliminate the bacteria that causes the disease of the organism. Usually the doctor indicates that the treatment must be done in 7 to 10 days, and the person must follow this treatment even if the symptoms no longer exist.
During treatment for gonorrhea it is important that the person avoids having sex until he is completely cured. In addition, the person's sexual partner should also be treated with antibiotics, even if they have no symptoms, due to the risk of transmitting gonorrhea to other people. See how gonorrhea treatment is done.
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther
Bibliography
- BRAZILIAN SOCIETY OF INFECTOLOGY. Gonorrhea. Available in: . Accessed on Aug 28, 2019
- BARER, Michael R et al. Medical Microbiology: A guide to microbial infections - pathogenesis, immunity, laboratory investigation and control. 19th ed. Elsevier, 2018. 264-266.
- PAPADAKIS, Maxine A .; MCPHEE, Stephen J .; RABOW, Michael W. Current Medical Diagnosis & Treatment 2019. 58th. NEW YORK: McGraw-Hill Education, 2019.
- BOSTON PUBLIC HEALTH COMMISSION. Gonorrhea. 2018. Available at:. Accessed on 14 Nov 2019
- MORGAN, Mackenzie K .; DECKER, Catherine F. Gonorrhea. Disease-a-Month. Vol.62. 260-268, 2016