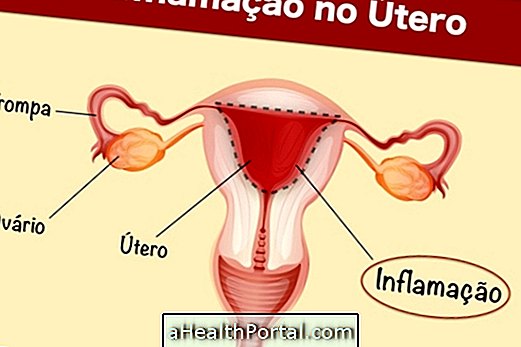
Chronic cystitis, also known as interstitial cystitis, corresponds to infection and inflammation of the bladder by bacteria, most often Escherichia coli, causing bladder pain, burning sensation when urinating and frequent urge to urinate, despite being in small amounts.
Symptoms of chronic cystitis usually appear at least 4 times a year and have a longer duration than the symptoms of acute cystitis and, therefore, the treatment should be more prolonged and involves the use of antibiotics, medicines to relieve the symptoms, lifestyle changes and bladder training.

Symptoms of chronic cystitis
Chronic cystic symptoms appear at least 4 times a year and are more lasting compared to acute cystitis, the main ones being:
- Bladder pain, especially when it is full;
- Frequent desire to urinate, although urine is eliminated in small amounts;
- Burning sensation when urinating;
- Cloudy or bloody urine;
- Low fever in some cases;
- Increased sensitivity of the genital region;
- Pain during sexual intercourse;
- Pain during ejaculation, in men, and menstruation, in the case of women.
It is important that the person see the urologist or gynecologist if he presents the signs and symptoms of chronic cystitis, as it is possible for the doctor to make the diagnosis and indicate the appropriate treatment.
In addition to assessing signs and symptoms, the doctor recommends that certain tests be carried out to confirm chronic cystitis, such as type 1 urine test, EAS, urine culture and imaging tests, such as pelvic region ultrasound and cystoscopy, which it is a test to evaluate the urinary tract.
Possible complications
The complications of chronic cystitis are related to lack of treatment or incomplete treatment, because in these cases the bacteria responsible for cystitis continues to multiply and are more likely to reach the kidneys, which can result in renal failure.
In addition, if the kidneys are compromised, there is also a greater chance of the bacteria reaching the bloodstream, resulting in sepsis, which corresponds to a serious health situation, since the bacteria in the bloodstream can reach other organs and cause changes in functioning, representing a risk to life. Understand what sepsis is and how to identify it.
How is the treatment
Chronic cystitis has no cure and, therefore, treatment aims to relieve symptoms and prevent complications. Thus, it is recommended that the treatment be done according to the doctor's instructions, and should be continued even if there are no more symptoms, unless the interruption is guided by the doctor, as this way it is possible to reduce the risk of complications.
It is important that the microorganism responsible for cystitis is identified, as it is thus possible to indicate the most appropriate antibiotic for its elimination. In addition, remedies are indicated to help reduce inflammation of the bladder and thus relieve symptoms of cystitis, such as antispasmodics and analgesics.
In addition, as in chronic cystitis, the person has an excessive urge to urinate, the doctor may recommend treatments to reduce the urge to urinate and relax the bladder and change some habits such as reducing stress, improving eating habits and eating. of water during the day and increased frequency of physical activity, as these factors can interfere with the intensity of symptoms.
See more details about the treatment for cystitis.
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther
Bibliography
- UROLOGY CARE FOUNDATION. What is Interstitial Cystitis (IC) / Bladder Pain Syndrome?. Available in: . Accessed on 26 May 2020