The itchy skin occurs due to some type of inflammatory reaction, either because of cosmetic products, such as makeup, or by eating some type of food, such as pepper, for example. Dry skin is also one of the reasons that causes a person to feel itchy skin, in addition to being able to identify areas of flaking, and it is necessary to apply moisturizing cream after the bath to improve.
When the itch lasts for more than 1 month and does not improve with any homemade measure, it is necessary to consult a dermatologist, as it may be a sign of some disease, such as dermatitis, infections and problems in the liver or gallbladder and the treatment depends on confirmation of the diagnosis. done by the doctor.

Thus, the main causes of itchy skin are:
1. Allergies
Some allergies can lead to itchy skin and are usually caused by irritants, which can be clothing made of synthetic materials and cosmetic products, such as makeup, creams and soaps.
In addition to itchy skin, allergies caused by these products can also lead to redness, swelling and flaking of the skin and if the person does not know exactly what is leading to the allergy symptoms it is important to consult a dermatologist to do an allergy test, such asprick test which is done by placing samples of certain substances on the skin to see how they react in the body. Understand what the prick test is and how it is done.
What to do: To relieve itchy skin caused by allergies it is important to avoid coming into contact with the product that causes the skin reaction, as well as avoid eating spicy foods, as it can also increase the itchy skin. Some measures can also help to reduce this symptom, such as taking anti-allergens, using hypoallergenic soap, with low pH, bathing in warm water and giving preference to cotton clothes.
2. Dermatitis
Itchy skin can indicate some type of dermatitis, such as atopic dermatitis, which is an inflammatory skin disease that leads to the appearance of eczema, which is characterized by red flaking plaques, and in some cases may appear in the form of vesicles.
Contact dermatitis is another type of skin inflammation that causes itching and redness in the skin, which can be caused by exaggerated reactions of the defense cells when they come into contact with certain substances, such as jewelry, plants, food dyes and beauty products or cleaning.
What to do: to confirm the diagnosis of dermatitis and differentiate which type the person has, it is necessary to consult a dermatologist to assess the symptoms and indicate the most appropriate treatment, which can be done with antiallergic agents, corticosteroid ointments, such as 1% hydrocortisone , or with corticosteroids to take.
In addition, applying cold compress of chamomile is a homemade option that can be used to relieve the itchiness caused by dermatitis. See other options for home remedies for dermatitis.
3. Dry skin
Dry skin, scientifically known as xeroderma, is more common in elderly people, but it can appear in anyone, especially in periods of dry and cold weather and as a consequence of the use of water-based cosmetics and very strong chemicals. When the skin is dry it can cause severe itching of the skin, in addition to leading to flaking, cracking and redness.
What to do: to relieve itchy dry skin it is necessary to apply moisturizers after bathing, as in this situation the absorption of the product is greater and it is also important that the person increase their water intake and on very dry days use a humidifier in the environment.
4. Stress and anxiety
Excessive stress and anxiety causes substances known as cytokines, which are responsible for the body's inflammatory response, to be released and therefore can cause skin reactions, leading to itching and redness of the skin.
In addition, these feelings cause people who already have skin diseases, such as dermatitis, to have their symptoms worsened, because it causes the activation of cells of the immune system in an exaggerated way, leading to increased itching of the skin, for example.
What to do: To alleviate the itchy skin that happens because of stress and anxiety, the ideal is to adopt measures to reduce these symptoms, which can be through physical activities, meditation, psychotherapy and if that is the case, the symptoms are still necessary consult a psychiatrist, who may recommend the use of antidepressants.
Watch a video with other tips on how to control anxiety and stress:

5. Liver and gallbladder problems
Some problems in the liver and gallbladder cause a reduction in the production and flow of bile, which is a fluid produced in these organs responsible for the absorption of fats, and this can happen due to obstruction in the bile ducts and liver channels.
Thus, with the accumulation of bile in the body, the levels of bilirubin, which is a component of bile, are greatly increased, causing symptoms such as yellowish skin and eyes and itchy skin, which is more intense at night and can be more localized in women. soles of the feet and in the palm of the hand.
Cholestasis gravidarum is a liver disease that can arise during pregnancy, which has these characteristics, and it may be necessary to perform magnetic resonance imaging or ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis.
What to do: After confirming the diagnosis of the disease that causes the problem in the liver or gallbladder, the doctor may prescribe medications to stimulate the production of bile acids that help to balance the levels of fat in the bile. In these cases, it is also important to avoid the consumption of alcohol and caffeinated beverages, just as a balanced diet, low in fats, should be made.
6. Autoimmune diseases
Lupus is a type of autoimmune disease that is characterized by the production of excess antibodies, which can cause symptoms such as irritation, redness and itching of the skin and in the most severe cases, can reach other organs such as the lung and cause chest pain and shortness of breathe.
Like lupus, psoriasis is a disease caused by the action of cells against the organism itself, as they understand the body as an invading agent. Thus, they begin to attack certain organs, including the skin, leading to flaking, the appearance of red spots and itchy skin. Know the types of psoriasis and the main symptoms of each.
What to do: both lupus and psoriasis are diseases that cannot be cured, but the symptoms can be controlled through ointments and medications with corticosteroids or immunosuppressants indicated by the rheumatologist.
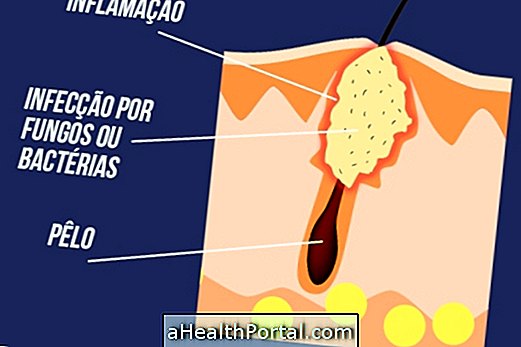
7. Infections
The itchy skin may be the result of infections caused mainly by bacteria of the typeStaphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes and Candida albicans. Folliculitis is a type of skin infection that causes the appearance of red pellets, with itchy pus that occur due to inflammation and the presence of bacteria at the root of the hair.
Herpes is also a type of infection, however it is caused by viruses, and can cause symptoms such as itchy skin, redness and the presence of blisters. In addition, skin infection can also be caused by fungi, such as mycoses that arise mainly in the fold regions, such as under the arm and between the toes, causing severe itching of the skin. Learn more about ringworm on the foot and how to treat it.
What to do: if itchy skin for more than a month, it is necessary to consult a dermatologist to examine the skin and check for infections, because if it does, antibiotics for bacterial and anti-fungal infections may be recommended to eliminate fungi. Herpes cannot be cured, but the person does not always have skin lesions, which usually appear when immunity is low, and acyclovir ointment may be indicated by a doctor.
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther
Bibliography
- BRAS, Susana; AMARO, Cristina; CARDOSO, Jorge. Chronic itching. Revista da SPDV 72 2014 ;. Vol.72, n.4. 1-19, 2014
- ANTUNES, Adriana A. et al. Practical guide for updating atopic dermatitis - Part I: etiopathogenesis, clinic and diagnosis. Arq Asma Alerg Immunol. Vol.1, n.2. 131-156, 2017
- ROSMANINHO, Isabel; MOREIRA, Ana; SILVA, José P. M. Contact dermatitis: literature review. Rev Port Immunoallergology. Vol.24, n.4. 197-209, 2016
- BRAZILIAN SOCIETY OF HEPATOLOGY. Itching in liver disease. Available in: . Accessed on 20 Feb 2020
- MINISTRY OF HEALTH. Clinical Protocol and Therapeutic Guidelines for Primary Biliary Cholangitis. Available in: . Accessed on 20 Feb 2020
- CALADO, Gisela; LOUREIRO, Graça et al. Stress and allergic disease: Underlying mechanisms. Rev Port Immunoallergology. Vol.20, n.1. 9-21, 2012
- LUDWIG, Martha W.B. et al. Lesion location and stress levels in dermatological patients. Psychology Studies. Vol.25, n.3. 343-352, 2008
- VIRTUAL HEALTH LIBRARY. Psoriasis. Available in: . Accessed on 20 Feb 2020
- MINISTRY OF HEALTH. Lupus: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention. Available in: . Accessed on 20 Feb 2020