The symptoms of HIV in the baby are mainly related to the appearance of recurrent infections, but they can be difficult to identify.
Some symptoms of HIV in your baby may be:
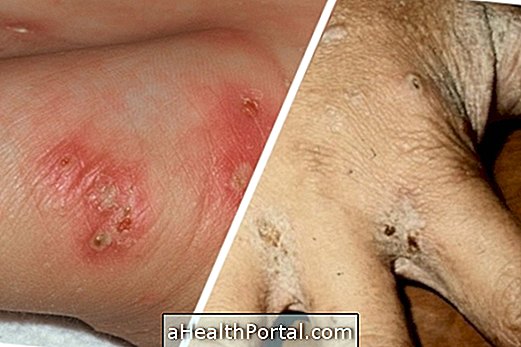
- Recurrent breathing problems, such as sinusitis;
- Swollen tongues in different places of the body;
- Mouth infections such as oral thrush or thrush;
- Delay in development and growth;
- Frequent diarrhea;
- Persistent fever;
- Serious infections such as pneumonia or meningitis.
Symptoms of HIV in the baby are more frequent in children of HIV-positive mothers, especially when antiviral treatment is not given during pregnancy.
Symptoms usually appear around 4 months of age, but can take up to 6 years to appear, and treatment should be started according to your pediatrician's appointment.
Treatment for HIV in the baby
Treatment for HIV in the baby should be done by a pediatrician-appointed infectious disease physician and includes the ingestion of oral antiviral remedies in the form of syrup.
Usually, treatment is started when there are symptoms of HIV or when the child is over 12 months old and the immune system is very weak.
Throughout the treatment, the antiviral can be altered, since it must be adapted according to the observed results.
Useful link:
- How to care for the baby with HIV