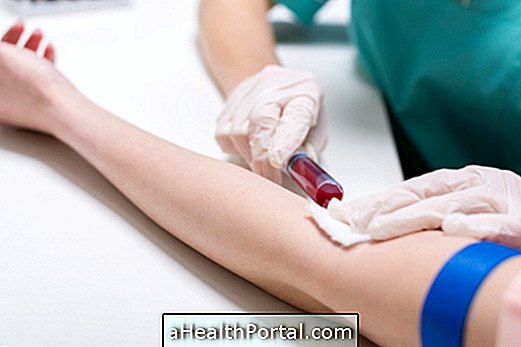
Symptoms of anemia include frequent tiredness, lack of disposition, and pale skin, which may be related to lack of iron in the blood due to some eating deficiency or persistent bleeding. It is usually easy to identify the anemia through the person's symptoms and the blood test to assess the amount of hemoglobin, being considered anemia when the value is less than 12 g / dL in women or 13 g / dL in men.
People who eat a variety of foods, and who regularly eat foods such as beans and red meat, are less likely to suffer from anemia, but the best way to confirm them is by taking a blood test. The following are the symptoms of anemia:
- Easy fatigue;
- Pale skin;
- Lack of disposition;
- Headache;
- Irritability;
- Restless legs at night;
- Low motor and cognitive development in the baby;
- Low productivity at work;
- Low muscle strength and difficulty gaining muscles;
- In pregnancy there is an increased risk of prematurity and low birth weight;
- Atrophy of the tongue papillae;
- Willingness to eat clay, earth, paper, soap, clay ...
The symptoms of anemia begin slowly, causing adaptation, so the person may take some time to realize the onset of anemia.

Iron deficiency anemia is a blood iron deficiency, which is very common all over the world. It can be caused by low iron intake and prolonged bleeding, such as heavy menstruation, or bleeding within the digestive system due to gastric ulcer, for example. Each mL of lost blood results in a reduction of about 0.5 mg of iron.
Other conditions that can also cause iron deficiency anemia are blood donation, major surgery, hemodialysis, and high-performance sports.
How to confirm anemia
The blood test that confirms the anemia is the blood count and the ferritin dosage. Iron deficiency anemia is considered when:
| Age | Values |
| Children between 2 and 3 years old | below 11.5 g / dL |
| Children up to 4 years | below 11 g / dL |
| Children between 5 and 11 years old | below 11.5 g / dL |
| Children between 12 and 14 years old | below 12 g / dL |
| 15+ years |
below 7 to 12 g / dL (light) below 7 g / dL (severe) |
| Adult women | below 12 g / dL |
| Adult men | below 13 g / dL |
| Gestation | between 9 and 11 g / dL (light) between 7 and 9 g / dL (moderate) below 7 g / dL (severe) |
| Post childbirth | below 10 g / dL in the first 48 hours below 12 g / dL in the first weeks |
| Seniors | below 13.2 g / dL for men below 12.2 g / dL for women |
| Black adults | below 12.7 g / dL for men below 11.5 g / dL for women |
Normal ferritin levels range from 40 to 200 ng / mL (mcg / L) but ferritin may be increased in case of inflammatory, infectious, malignant, or hepatic diseases.
Check other tests to confirm the type of anemia.
How to fight anemia
Anemia treatment can be done by taking iron supplements in the most severe cases, and by increasing the consumption of iron-rich foods.
Diet for anemia
One should eat more foods like red meats, viscera such as liver and kidneys, poultry meats, fish and dark green vegetables. People who consume animal products have a lower risk of developing iron deficiency anemia than vegetarians.
To increase the absorption of iron it is recommended to consume vitamin C in the same meal, as orange, acerola and lemon, and being careful not to drink tea or coffee, soon after, because they make this absorption difficult.
Check out what should be feeding in case of anemia in the following video:

Here are some examples of teas and juices against anemia
Supplement of iron against anemia
For treatment it is recommended to take the iron supplement as follows:
- 180 to 200 mg of elemental iron per day for adults;
- 1.5 to 2 mg of elemental iron per day for children;
Doses should be divided into 3 to 4 shots, preferably 30 minutes before lunch and dinner.
As a form of prevention of anemia the doctor may also recommend iron supplementation during pregnancy and in pre-school children. The indicated dose is approximately:
- 100 mg of elemental iron per day for pregnant women and women who breastfeed;
- 30 mg of elemental iron per day for preschoolers and
- 30-60 mg of elemental iron per day for school children, in periods of two to three weeks, at least 2 times a year.
After starting treatment with iron supplementation, after about 3 months, the tests should be repeated to check if the anemia has disappeared.