Brown discharge is normal after menstruation because it is common to get some blood clots until a few days after the end of menstruation. In addition, brown discharge is also common after intimate contact or due to irritation of the walls of the vagina, especially during menstruation or pregnancy.
However, brown discharge when it lasts for more than 3 days may also indicate the presence of vaginal infections, such as trichomoniasis, which arise especially when vaginal pH is altered by frequent vaginal douches, for example.

When brownish discharge is normal
Brown discharge is normal in the following situations:
- In adolescence;
- After intimate contact during pregnancy;
- In the first few days after menstruation;
- When the woman has hormonal changes;
- Change of contraceptive or
- Take hormone medications for thyroid, for example.
However, if the discharge happens in large quantity or for more than 4 days it is recommended to consult the gynecologist to start the appropriate treatment.
Can brown discharge be pregnancy?
Normally brown discharge is not a sign of pregnancy because it is more common that, at the beginning of gestation, the woman has a small rosy discharge that indicates the implantation of the fetus in the uterus. Find out what may be the first signs of pregnancy: 10 first symptoms of pregnancy.
However, in women who are pregnant the output of a dark fluid similar to menstruation and brown discharge may indicate blood loss through the vagina, and this should be evaluated by the obstetrician, especially if it has foul smelling or other symptoms such as abdominal pain, itching or heavy bleeding. This change may indicate, among other possibilities, ectopic pregnancy, for example. Find out what brown discharge means in pregnancy.
If you suspect complications in pregnancy confirm your symptoms in the article: Pregnancy complications.

5 diseases that cause brown discharge
Some of the possible causes of brown discharge include irritation of the cervix, pelvic inflammatory disease, or ovarian cyst. See more causes and how to treat each of these diseases.
1. Irritation of the cervix
The cervix is a very sensitive region and some common situations such as pap smears or frequent sexual contact may cause this symptom.
- How to treat: No specific treatment is necessary because the amount of secretion is low and no other symptoms are present. Keeping the region clean and dry may be sufficient to control this discharge in less than 2 days. However, it is necessary not to have intimate contact until the discharge has disappeared.
2. Pelvic inflammatory disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease refers to inflammation in a woman's internal genitalia, such as endometritis, salpingitis, bacterial vaginosis, or inflammation of the ovaries. Situations that can cause dark discharge, pelvic pain and during intimate contact, which often appear during or after menstruation, or a few days or weeks after being contaminated with an STD.
- How to treat: After performing tests to identify what is causing this inflammatory disease, the gynecologist may indicate the use of oral antibiotics or use as an ointment to introduce into the vagina. Medications for fever and anti-inflammatories may also be recommended; if there is no improvement of symptoms within 3 days, the doctor can replace the medications with others. As these diseases are usually transmitted sexually you can not have intimate contact until you finish the treatment. Learn the names of some remedies for pelvic inflammatory disease.
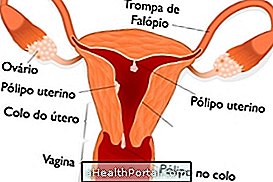
3. Ovary cyst
Cyst in the ovary can cause uterine bleeding before or after menstruation, which mixed with the woman's natural secretions can become a brown discharge, but often there are other symptoms such as pain during ovulation, pain during or after intercourse, bleeding vaginal discharge outside of menstruation, weight gain and difficulty getting pregnant.
- How to treat: Specific treatment is not always necessary, because the appearance of cysts in the ovary is a common situation in young women, but the gynecologist may indicate taking the contraceptive pill. In more severe cases it may be necessary to withdraw the ovary to avoid further complications such as torsion of the ovary or cancer, for example. Learn all about the types of ovarian cysts and other common questions.
4. Polycystic ovarian syndrome
In the polycystic ovary syndrome it is common to have dark discharge that is due to the presence of uterine blood, in addition to others such as irregular menstruation, excess hair and acne.
- How to treat: Treatment can be done with the use of the contraceptive pill to regulate menstruation and to control the hormonal irregularities, indicated by the gynecologist, since it is not any pill that can be used. Check out two teas that may help treat this syndrome.
5. Cancer of uterus
Cancer of the uterus can cause brown discharge, in addition to other symptoms such as bleeding before, during or after menstruation, and pain in the pelvic region after intercourse, for example. Check out more symptoms that may indicate uterine cancer.
- What to do: If you suspect you should go to your gynecologist for tests such as a pap smear and colposcopy, and check if it really can be cancer and then indicate the most appropriate treatment, which may be conization, brachytherapy, radiotherapy, or surgery for uterus, depending on the staging of the tumor.
When to go to the gynecologist
It is recommended to consult a gynecologist when the brown discharge:
- Lasts more than 3 days;
- It is accompanied by other symptoms such as abdominal pain, foul smell or itching;
- It is interspersed with bright red bleeding.
In these cases the doctor will diagnose the problem by observing the discharge by seeing the inside of the woman's panties, inserting the vaginal speculum to check the interior of the female intima and then recommending the appropriate treatment.
How to prevent vaginal discharge
To prevent dark discharge it is recommended to avoid the use of intimate showers by washing the outside of the vagina daily only during bathing or after intimate contact. The panties should preferably be cotton so the area is always drier, and shorts and tight jeans should also be avoided because they clog the place, facilitating perspiration and the proliferation of micro-organisms that cause infections.