Normally, the premature infant is placed in the neonatal intensive care unit until he is able to breathe on his own, weighs more than 2 kg and develops the suction reflex, which means that some babies may be hospitalized longer than others.
After this period the premature baby can go home with the parents and can be treated similarly to term babies. However, if the baby has some kind of health problem, parents should adjust the care according to the doctor's instructions.
See the most important care with your baby at: What to do to take care of the newborn at home.


What exams the premature baby needs to do
During the neonatal intensive care unit, the preterm infant will be tested regularly to ensure that it is developing properly and to diagnose problems early, which when treated can be permanently cured. So the tests normally done include:
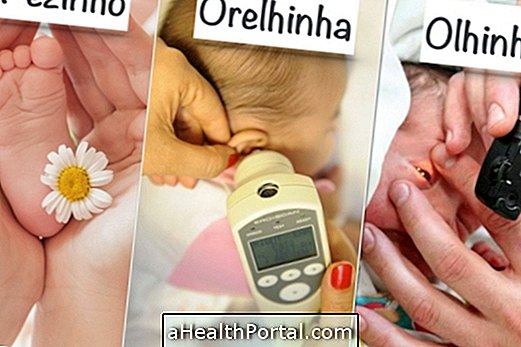
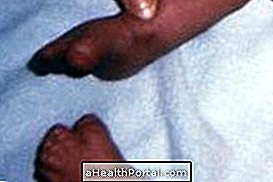
- Foot test: a small prick is made in the premature heel to remove blood and test for the presence of some health problems such as phenylketonuria or cystic fibrosis. Learn more: Test the foot.
- Hearing tests: are done within the first 2 days after birth to assess if there are developmental problems in the baby's ears;
- Blood tests are done throughout the ICU stay to assess blood oxygen levels, helping to diagnose problems in the lungs or heart, for example;
- Vision exams: These are done soon after the birth of the premature infant to assess the presence of problems such as retinopathy or strabismus of the retina and should be done up to 9 weeks after birth to ensure that the eye is developing properly;
- Ultrasound examinations are done when your pediatrician suspects changes in the heart, lungs, or other organs to diagnose the problem and initiate appropriate treatment.
In addition to these exams, the premature baby is also evaluated physically every day, with the most important parameters being weight, head size and height.
When to vaccinate the premature baby
The premature baby's vaccination program should only be started when the baby is older than 2 kg and therefore the BCG vaccine should be delayed until the baby reaches that weight.
Know when to give the other vaccines: Baby vaccination schedule.
However, in cases where the mother has hepatitis B the pediatrician may decide to vaccinate before the baby reaches 2 kg. In such cases, the vaccine should be divided into 4 doses instead of 3, and the second and third doses doses should be made one month apart and the fourth, six months after the second.


How To Care for Premature Baby at Home
Caring for a premature baby at home can be a challenge for parents, especially when the baby has some respiratory or developmental problem. However, most care is similar to full-term babies, the most important of which are related to breathing, infection risk, and feeding.
How to avoid breathing problems in premature
During the first 6 months of life there is a high risk of breathing problems, especially in premature babies, as the lungs are still developing. One of the most common problems is sudden death syndrome, which is caused by asphyxia during sleep.
To reduce this risk, you should:
- Always lay the baby on his or her belly upwards, placing the baby's feet against the bottom of the crib;
- Use lightweight sheets and blankets in the baby's crib;
- Avoid using cushion in baby's crib;
- Keep the baby's crib in the parents' room until at least 6 months of age;
- Do not fall asleep with the baby on the bed or on the sofa;
- Avoid having heaters or air conditioning near the baby's crib.
In addition, if the baby has some type of respiratory problem, it is important to follow the instructions given at the maternity unit by the pediatrician or the nurses, which may include nebulisations or nose drops, for example.
How to ensure the correct temperature for the premature
The premature baby has more difficulty keeping his body temperature controlled so he can get cold quickly after bath or get very hot when he has a lot of clothes, for example.
Here's how to dress in: How to dress the baby.
Thus, it is recommended to always keep the house at a temperature between 20 and 22º C and dress the baby with several layers of clothing so that one can remove one when the room temperature gets warmer or another layer of clothing is added when the day gets colder.
How to reduce the risk of infections in premature baby
Premature babies have a poorly developed immune system and therefore, in the first months of age, they present an increased risk of infection. However, there are some precautions that help decrease the chances of infections, which include:
- Wash hands after changing diapers, before preparing food and after going in the bathroom;
- Ask visitors to wash their hands before being in contact with the premature baby;
- Try to avoid many visits to the baby during the first 3 months;
- Avoid going with the baby to places with lots of people, such as shopping centers or parks, in the first 3 months;
- Keep pets away from the baby during the first few weeks.
So the best environment to prevent infections is to stay at home as it is an easier environment to control. However, if you need to leave, you should give preference to places with less people or at times that are more empty.
How To Feed Your Premature Baby
In order to feed the baby prematurely at home, parents usually receive teachings in the maternity ward, as it is common for the baby to not be able to nurse alone in the mother's breast, needing to be fed by a small tube in a technique called relactation. Here's how it's done: How to relay.
However, when the baby is able to hold the mother's breast, it can be fed directly from the breast, and for this, it is important to develop a correct technique to help the baby to nurse and prevent the development of problems in the mother's breast. See breastfeeding tips in: How to breastfeed.