Sometimes the difficulty in communicating can be caused by a problem called aphasia, which is common during migraine attacks or when you suffer from a more severe brain injury such as stroke, tumor, head injury, or Alzheimer's.
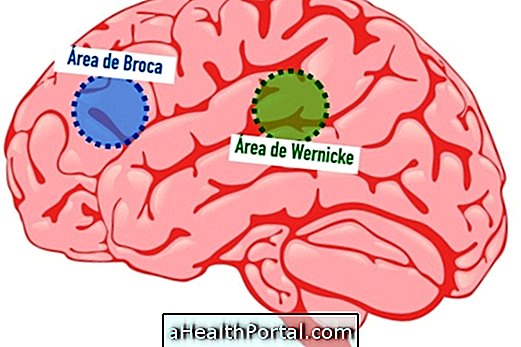
It is a neurological change in one of two areas of the brain, known as Broca or Wernicke, which impairs the ability to speak and understand, and may be temporary, as in the case of migraine with aura, or permanent, in cases of people who have had a stroke or suffer from Alzheimer's, for example.
In these cases, a speech therapist should be consulted to begin treatment that helps to develop the affected brain sites and to adopt strategies to communicate effectively in the day-to-day, treating Wernicke's Aphasia of Broca or Aphasia.
Thus, although it seems very difficult to communicate with someone with aphasia, some tips can facilitate coexistence, decrease frustration, and improve the patient's quality of life.
Tips for family and friends to make communication easier
- Use simple phrases and speak slowly;
- Allow the other person to speak without having to hurry;
- Do not try to complete the phrases of the person with aphasia;
- Avoid background noise such as connected radio or open window;
- Use drawings and gestures to explain an idea;
- Avoid excluding the patient with aphasia from the conversations.
In addition, it may be important to note the types of changes and the reaction of the patient with aphasia, so that physicians can adapt treatment techniques to make coexistence less limited.
Usually, in cases of aphasia, the patient may also have difficulty swallowing the food, so see how to get around the problem in: What to eat when I can not chew.
Tips for aphasia who can communicate better
- Always have in your purse or wallet a card explaining that you have aphasia;
- To tell that you have aphasia during times of migraine, for example, so that the people with whom you live know how to act in a crisis;
- Have a small notebook and pen to be able to express ideas through drawings, whenever it is necessary to communicate;
- Create a small book of words, pictures and expressions that you use frequently;
- Adopt universal gestures like "stop", "jewel", "ok" or "there".
However, the difficulty of communication can also be caused by other completely different factors, such as deafness, depression, or delay in the development of communication skills, such as in Down syndrome. In these cases, these techniques are not used and the professionals who accompany each patient should guide the most appropriate treatment.

How is the treatment of aphasia in the audiologist
The treatment of aphasia is initiated, in most cases, with language therapy sessions in a speech-language pathologist's office, stimulating the affected brain sites. In these sessions, the speech therapist can ask the patient to try to express himself using speech only, without being able to use gestate or drawings, for example.
In other sessions, the speech therapist can teach how to properly use some of these techniques, such as making gestures, drawing or pointing at objects, to communicate better.
How To Know if It Is Aphasia
Aphasia can cause difficulty speaking what you want or difficulty understanding what others are talking about and therefore the most common symptoms include:
Difficulty talking - Broca's Aphasia
- Difficulty in using the words one wants to say;
- Replace words with others that may or may not be related, for example replace "fish" with "book";
- To change the sound of some words like "washing machine" by "maquina lashima";
- Speak words that do not exist, like "jupir" instead of "bread";
- Difficulty creating sentences with more than 1 or 2 words;
- Mix in a sentence words that do not exist with others that make sense.
Difficulty understanding - Wernicke's aphasia
- Misunderstand what others are talking about, especially when they speak faster;
- Not being able to see what the other is talking about when there is a bit of noise, like having the television on or the window open;
- Literally understand jokes or popular expressions like "it is raining knives";
- Difficulty reading books or other written material;
- Difficulty understanding the concept of numbers, such as knowing what time it is or counting money;
These symptoms vary according to the affected site of the brain, and when the change occurs in the area of Broca, for example, the appearance of difficulty speaking is more common. Already when the change happens in the area of Wernicke, it is more frequent to arise problems of understanding.