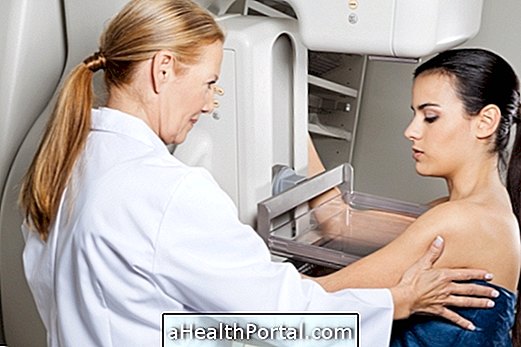
Breast biopsy is a diagnostic test in which the doctor removes a piece of tissue from the inside of the breast, usually a lump, to evaluate in the laboratory and see if there are any cancer cells.
This test is usually done to confirm or misdiagnose breast cancer, especially when other tests such as mammography or MRI have indicated changes that may indicate cancer.
The biopsy can be done in the gynecologist's office with the application of local anesthesia and, therefore, the woman does not need to be hospitalized.
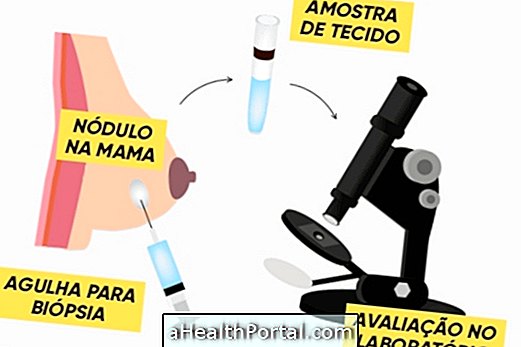
How is the biopsy done?
The procedure for breast biopsy is relatively simple. For this, the doctor:
- Apply local anesthesia in a region of the breast;
- Insert a needle into the anesthetized region;
- Collects a piece of tissue from the lump identified in other tests;
- Remove the needle and send the tissue sample to the laboratory.
Often, the midwife may use an ultrasound device to help guide the needle to the nodule, ensuring that the sample is removed from the correct location.
In addition to biopsy of the lump in the breast, the doctor may also perform a biopsy of a lymph node, usually in the armpit region. If this happens, the procedure will be similar to that of breast biopsy.
When surgery is needed
Depending on the size of the lump, the woman's history, or the type of changes identified on the mammogram, the doctor may also choose to undergo a small biopsy. In these cases, the surgery is done in a hospital with general anesthesia and may already include total removal of the lump.
Thus, if the presence of cancer is confirmed, the woman may no longer need to undergo surgery, and can start treatment with radio or chemotherapy, to eliminate remains of malignant cells that have remained in the breast.
Does breast biopsy hurt?
Since local anesthesia is used in the breast, the biopsy usually does not cause pain, however, it is possible to feel pressure on the breast, which, in more sensitive women, can cause some discomfort.
Generally, the pain is felt only during the small bites that the doctors does on the skin to introduce the anesthesia in the breast.
Main care after biopsy
In the first 24 hours after the biopsy it is recommended to avoid strenuous physical activity, but the woman may return to normal daily tasks such as working, shopping or tidying up the house, for example. However, it is important to see your doctor if, during the first few days, symptoms such as:
- Breast swelling;
- Bleeding at the biopsy site;
- Redness or hot skin.
In addition, it is common to have a small hematoma in the place where the needle was inserted, so your doctor may prescribe an analgesic or anti-inflammatory, such as Paracetamol or Ibuprofen, to relieve discomfort in the following days.
How to interpret the results
The result of the breast biopsy should always be interpreted by the doctor who requested the examination. However, the results may indicate:
- Absence of cancer cells : this means that the lump is benign and therefore, it is not cancer. However, the doctor may advise to keep vigilance, especially if the nodule has increased in size;
- Presence of cancerous or tumor cells : usually indicates the presence of cancer and also indicates other information about the lump that help the doctor to select the best form of treatment.
If the biopsy was performed with surgery and removal of the nodule, it is common that, in addition to indicating the presence or absence of cancer cells, the result also describes all the characteristics of the nodule.
When lymph node biopsy is positive and indicates the presence of tumor cells, it usually indicates that the cancer is already spreading from the breast to other sites.
How long does the result take?
Usually the results of breast biopsy can take up to 2 weeks, and the report is usually sent directly to the doctor. However, some labs may deliver the result to the woman herself, who must then make an appointment with the gynecologist to evaluate the meaning of the result.







-o-que--e-para-que-serve.jpg)




-causas-e-como-tratar.jpg)