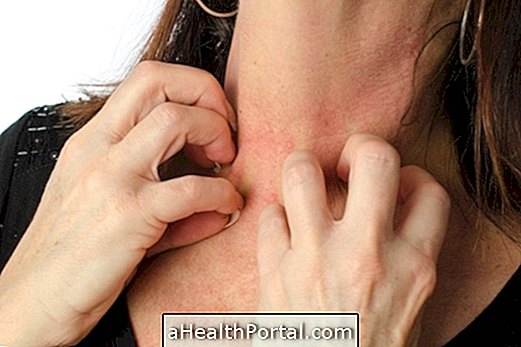
Eczema is an acute or chronic inflammation of the skin that causes symptoms such as itching, swelling and redness and may be caused by an allergy. This skin disease has no cure but can be controlled with the treatment indicated by the dermatologist.
This inflammation can occur in all ages, but they are more common in children and health professionals who tend to wash hands with antiseptic soap too often, which can hurt the skin.
Most Common Types
Eczema can be classified according to its cause in:
- Contact Eczema or Contact Dermatitis: Contact eczema is characterized by a skin injury that occurs due to contact with an aggressive agent, which may be a synthetic fabric or enamel, for example. This eczema is allergic, non contagious and should be treated with the use of antihistamine medicines to relieve itching and corticosteroid creams. In this case, it is important to avoid contact with the triggering agent of the frame. Learn more about contact dermatitis and how to treat it.
- Child Eczema: Child eczema manifests especially after 3 months of the baby, lasting until adolescence, but some may remain eczema into adulthood. The treatment is done with the use of corticosteroids or antihistamines, according to the pediatrician's orientation. Also, it is important to keep your skin hydrated.
- Atopic eczema or atopic dermatitis: Atopic eczema is an inflammation of the skin, usually of allergic origin, characterized by the presence of different lesions such as plaques or small reddish lumps that itch. The treatment is established by the dermatologist and is usually made with creams or ointments with corticosteroids. Here's how to identify and treat topical dermatitis.
- Nummular eczema or nummular dermatitis: This type of eczema is usually related to excessive dryness of the skin, due to cold or dry climate, for example. Nummular eczema is characterized by the presence of red and round spots on the skin that itch. Many times the treatment of nummular eczema involves the use of antibiotics, since there is a high chance of the person developing infections. Learn more about numeral dermatitis.
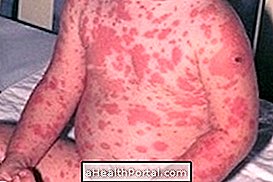
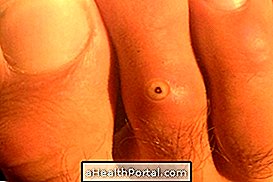
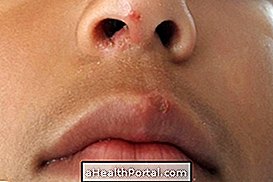
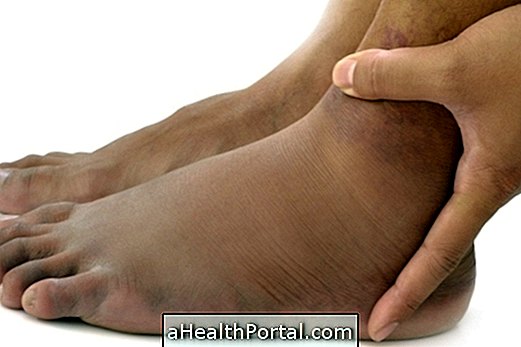
Eczema is an inflammation that is usually characterized by the presence of red spots that itch in the body, which then leads to the appearance of water-containing bubbles, characterizing the acute phase of the disease. In the chronic phase, these bubbles burst and release their contents and, after a while, dry up forming crusts, in addition to increasing the thickness of the skin.
How To Identify Eczema
Eczema usually arises in people who have very dry skin and is identified from the following characteristics:
- Redness on the spot;
- Itching;
- Presence of blisters on the skin;
- Swelling;
- Desquamation of the skin;
- Presence of crusts.
In infants and children eczema is more common on the cheeks, arms and legs, but in adults the symptoms can arise in any part of the body.
How is the treatment done?
The treatment for eczema is determined by the dermatologist and depends on the type of injury, severity and age of the person, and can be done using an antiallergic remedy to calm the itching and facilitate sleep, ointment or cream with corticosteroids such as hydrocortisone and antibiotics for bacterial infections.
During treatment it is important to keep the skin moisturized, as dry skin is one of the risk factors for worsening symptoms. Here's a good home remedy for eczema.