Donovanose, also known as inguinal granuloma or venereal granuloma, is an infectious-contagious disease caused by the bacterium Klebsiella granulomatis, formerly known as Donovani granulomatis and Claymmatobacterium granulomatis, characterized by the presence of lumps or wounds that bleed easily mainly in the genital region.
The best way to prevent donovanose is through the use of condoms during sexual intercourse. However, in the case of lesions in the inguinal or perianal region, it is important to consult the physician for the diagnosis and initiation of treatment, since the bacteria are present in the lesion.

Symptoms of donovanose
Donovanose manifests itself from the following symptoms:
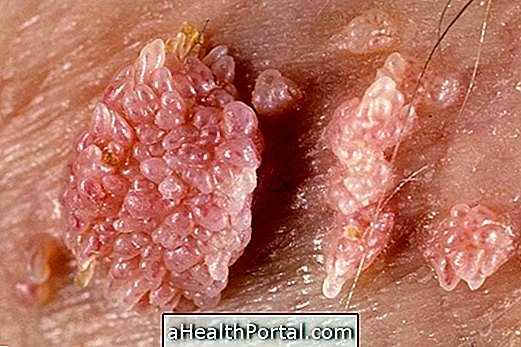
- Lumps or wounds in the genital, inguinal or perianal region;
- Wounds or lumps of bright red appearance that grow and can bleed easily;
- Presence of ulcer;
- Wound that looks well defined and does not hurt.
Symptoms can occur between 30 days and 6 months after infection by the bacteria and so the treatment can be delayed, which can worsen infection and even facilitate the entry of other microorganisms into the body and give rise to an infection blood. Understand what the infection is in the blood and how to treat it.
The initial diagnosis is made from the microbiological analysis of the wound secretion, in which the bacterium is identified and the profile of sensitivity and antibiotic resistance, so that the doctor can indicate the most effective medicine to fight the infection. The doctor may also request confirmation of donovanose by biopsy of the tissue of the affected areas. Find out what the biopsy is for.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment for donovanose is done according to medical advice, and it is usually recommended to use antibiotics, such as:
- Doxycycline for at least 3 weeks;
- Sulfamethoxazole / Trimethoprim, at least 3 weeks;
- Ciprofloxacin until it is no longer possible to identify Klebsiella granulomatis ;
- Tianfenicol granulate, until there is no more evidence of the bacteria;
- Erythromycin for at least 3 weeks.
It is important to point out that the choice of antibiotic and the time of use should be indicated by the doctor and the consumption of antibiotics without the advice of the responsible doctor is not indicated.
In the case of more extensive lesions, surgical removal may be recommended. In addition, during and after treatment it is important to perform periodic examinations so that you can see how the body is reacting to the treatment and whether the bacteria are being eliminated. It is also indicated that the person being treated does not have sex until bacteria are identified, to avoid the possible contagion of other people.