Cor pulmonale corresponds to a change in the right ventricle due to lung disease. The right ventricle is a structure belonging to the cardiovascular system responsible for transporting blood from the heart to the lungs and can, due to lung diseases, mainly to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), suffer structural and therefore functional changes. Learn how to identify and treat COPD.
Cor pulmonale can be classified as acute or chronic:
- Cor pulmonale acute : may be caused due to pulmonary embolism or injury from mechanical ventilation and is usually easily reversible;
- Chronic cor pulmonale : is mainly caused by COPD, but may also be due to loss of lung tissue due to surgery, pulmonary fibrosis, disorders involving the respiratory muscles or due to chronic pulmonary embolism.
The diagnosis is made based on symptoms and laboratory and imaging tests, such as echocardiography, in which the cardiac structures are observed in real time, in which case structural alteration of the right ventricle is visualized.

Main causes
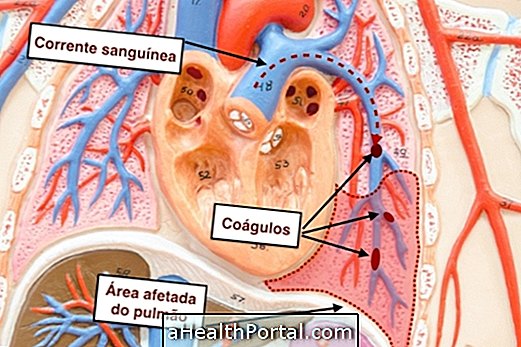
In the presence of pulmonary diseases, blood passes through the veins and pulmonary arteries with difficulty, characterizing pulmonary hypertension, which causes the cardiac structures, especially the right ventricle, to be overloaded.
Pulmonary hypertension and, consequently, cor pulmonale can be caused by:
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;
- Pulmonary embolism;
- Cystic fibrosis;
- Scleroderma;
- Pulmonary emphysema;
- Cardiac insufficiency
In addition, changes in vascularization and increased blood viscosity may result in pulmonary hypertension. Learn more about pulmonary hypertension.
Symptoms of cor pulmonale
Initially, cor pulmonale is asymptomatic, however non-specific symptoms may arise, such as:
- Extreme fatigue;
- Cyanosis;
- Cough with phlegm or blood;
- Difficulty or wheezing;
- Chest pain;
- Swelling of lower limbs;
- Liver enlargement;
- Dilatation of the jugular veins, which are the veins located in the neck;
- Yellow eyes.
Diagnosis is made by evaluating the symptoms and performing tests such as laboratory tests, such as arterial blood gases and blood counts, for example, electrocardiogram and echocardiogram, which is done to evaluate the heart structures in real time and can be perceived by means of this alteration in the right ventricle. Understand how the echocardiogram is done.
In addition, other tests may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis, such as chest tomography, pulmonary biopsy, and pulmonary vein angiography. See what angiotomography is for.
How is the treatment done?
The treatment of cor pulmonale is done according to the associated pulmonary disease, and it is usually recommended to improve oxygenation, reduce fluid retention, control pulmonary disease and improve the function of the right ventricle.
The use of drugs that improve circulation and decrease pressure within the lung, such as antihypertensives and anticoagulants, for example, may be recommended by the media. In more severe cases, however, cardiac or pulmonary transplantation may be necessary to resolve cor pulmonale.