Among the symptoms of meniscal injury are pain in the knee when walking, up and down stairs. The pain is located on the front of the knee and may reach the most lateral if the lesion is lateral meniscus or the innermost part of the knee if it is a lesion of the medial meniscus.
The treatment for meniscus recovery can be done through orthopedic surgery followed by physical therapy. At the beginning of the physiotherapeutic treatment the individual should rest, avoiding to move the leg, putting ice to reduce the pain. After a few days you can walk with the help of crutches and a knee brace. Gradually, with the work of physical therapy, the individual can return to his daily life normally.
The meniscus is a cartilage structure present in the knee that serves to protect the knees when there is an impact or a knock directly on the knee or leg, for example. This cartilage is very prone to injury in athletes, overweight people, with arthritis, arthrosis, or other problem that affects the knee joint.
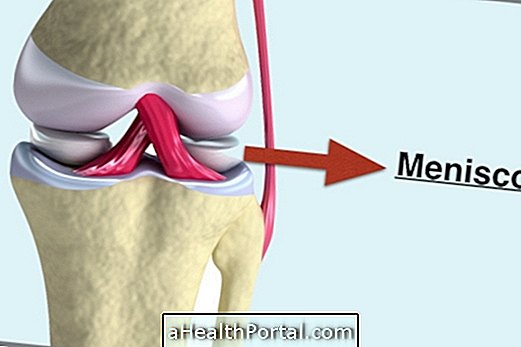
What Causes Injury
Meniscus injuries usually arise due to a strong knee bump, as in many types of sports such as football, basketball or tennis. However, there are some day-to-day situations that can also injure the meniscus such as:
- Turning the body very fast on one leg;
- Make squats very deep;
- Lift lots of weight using your legs;
- Hold your foot while walking.
With age, meniscal cartilage is becoming more weakened due to constant use and decreased blood circulation to the site, which can cause easier injury after age 65, even when going up or down stairs, for example.
Generally, lateral meniscus rupture is associated with rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament while rupture of the medial meniscus is associated with formation of the Baker's cyst. Lateral meniscus injury is more common in sudden movements as in a soccer game, whereas in the medial meniscus the lesion is formed by repetitive movements, and the lesion begins at the posterior part of the meniscus and can heal spontaneously without specific treatment .
Symptoms of meniscus injury
The main symptom of a meniscal injury is pain in the anterior and / or lateral region of the knee, which worsens or makes it difficult to climb up and down stairs. The pain is localized and can get worse as the days go by and can make walking even harder. In addition there is swelling of the sore area.
The orthopedist may request an x-ray to evaluate the knee but the best examination to diagnose a meniscal injury is MRI.
The physiotherapist will be able to identify a lesion in the meniscus through specific pain provocation tests carried out in the office.
Treatment to recover the meniscus injury

The treatment for a meniscus injury can be done with physical therapy or surgery in the most severe cases when it is necessary to have surgery to sew or cut the affected part of the meniscus, probably after surgery the doctor will leave the leg immobilized with a splint and will indicate the use of crutches and this immobilization should be maintained throughout the day and night, being withdrawn only in the bath and physical therapy. Learn what can be done in physiotherapy and exercises for meniscus injury.
After about 2 months of treatment the person needs to be checked and there is still local pain or movement limitation to be able to adjust the treatment. When the person no longer feels pain but can not fully bend the knee the exercises should have this goal. A good workout is to do squats, increasing the degree of knee flexion, the goal may be to try to squat to the maximum, until it is possible to sit on the heels.
Pain Relief Remedies
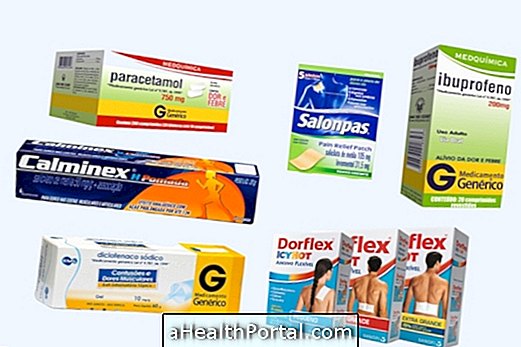
Medications should only be used after medical advice and are especially indicated after surgery. During the first few days after the operation, your doctor may advise you to use Paracetamol or Ibuprofen to relieve pain.
Ointments such as Cataflan and Voltaren may help in pain control but should not be applied until the wound is completely healed. A good way to relieve pain and swelling of the knee naturally is to apply a cold compress on the area while resting with your legs elevated.
How Food Can Help
During the recovery phase one should avoid consuming foods rich in sugar and increase the consumption of foods rich in proteins to facilitate the regeneration of tissues. It is also recommended to drink plenty of water to keep the body properly hydrated, which is also important to maintain lubrication of the knees. One should avoid fast food, soda and fried foods to avoid being overweight, which can hamper the recovery of this joint. See examples of healing foods.
How is the surgery to recover the meniscus
In ruptures of the lateral meniscus the orthopedist may indicate that surgery is performed soon to remove the affected part. However, when there is an injury to the medial meniscus, if it is longitudinal and small in size, the physician may choose to indicate physical therapy to see if the rupture can be cured.
When the meniscus is broken at its edges or when there is an injury in the middle of the meniscus, which separates into two parts, forming a kind of bucket, the doctor also indicates surgery soon, to prevent the injury from getting worse.
The surgery to repair the meniscus usually is done under local anesthesia, with arthroscopy, where the doctor only makes 3 holes in the knee, through which the equipment necessary to sew or remove the broken part of the meniscus enters. The surgeon can choose these from the forms of treatment:
- Sew the outermost part of the meniscus, because it is irrigated by the blood and so can regenerate;
- Remove the affected part of the meniscus, keeping the healthy part to prevent arthrosis from forming early.
It is not necessary to stay hospitalized but the recovery time varies from 2 to 3 weeks for the medial meniscus and 2 months for the lateral meniscus.
Signs of improvement and worsening
Signs of improvement come with the start of treatment and when the person follows all directions of the doctor and physiotherapist, taking the necessary rest and therapeutic exercises.
Complications
If the treatment is not performed, it is possible that the lesion worsens, and if the meniscus ruptures and the pain can limit the person's life, it is necessary to use analgesics and anti-inflammatories and to become accustomed to the pain throughout life. An injury to the meniscus can also lead to the formation of early arthrosis in the affected knee.