Sun exposure for longer than 1 hour or at times between 10am and 4pm can cause skin damage, such as burns, dehydration and risk of skin cancer.
This is due to the presence of UV and UV radiation emitted by the sun, which, when in excess, cause heating and damage to the skin layers.
Thus, the main effects of excess sun exposure are:
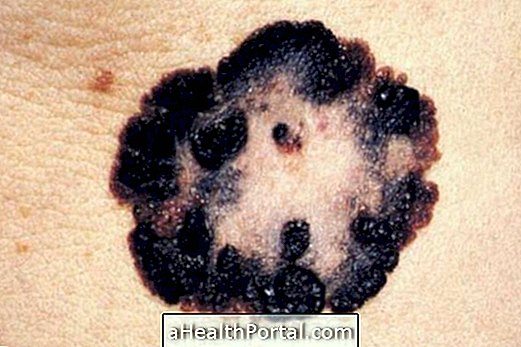
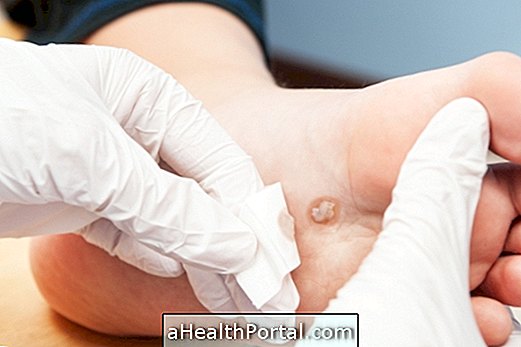
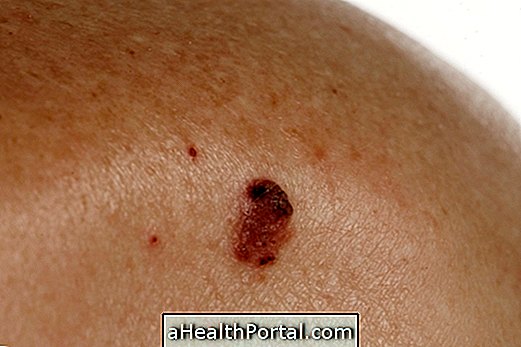
- Increased risk of skin cancer, which may be localized or malignant, such as melanoma;
- Burns, caused by heating the skin, which can become red, irritated and injured;
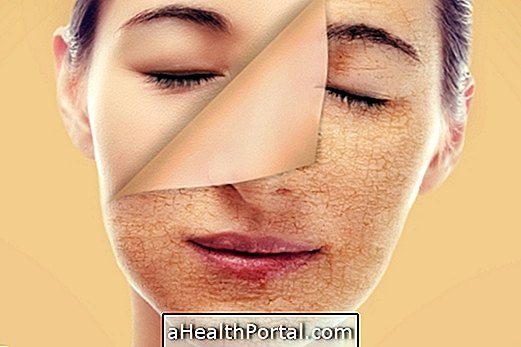
- Aging of the skin, which is caused by exposure to the sun's UV rays for long periods and for many years;
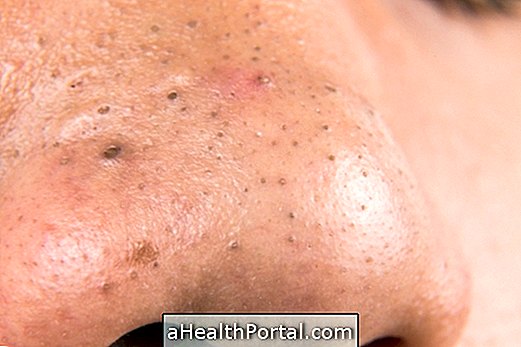
- Skin blemishes that may be dark, freckle-shaped, or have lumps or make the appearance of scars worse;
- Reduction of immunity is caused by too much exposure to the sun for many hours and unprotected, which can make the person more susceptible to illnesses such as influenza and colds, for example.
- Allergic reactions, with hives or reactions in products such as perfumes, cosmetics and lemon, for example, causing redness and local irritation;
- Damage to the eyes, such as irritation and cataracts, due to injuries to the eyes caused by excess sunlight;
- Dehydration, caused by loss of body water due to heat.
- Reaction to medications, which form dark spots due to interaction between the active principle of medicines such as antibiotics and anti-inflammatories, for example;
- It can reactivate the herpes virus in people who already have this disease, also due to changes in immunity.
Although sunbathing properly does good health, such as increased vitamin D and improved mood, these problems happen due to too much sun exposure or at times when the sun is too intense.

How to protect yourself
To avoid sun damage to the body, it is recommended to follow some guidelines, such as sunbathing before 10am and after 4pm, do not take more than 30 minutes of sunshine a day if the skin is clear and 60 minutes if the skin has a darker tone.
The use of sunscreen, FPS at least 15, for about 15 to 30 minutes before exposure, and replace after contact with the water or every 2 hours, in addition to being under the parasol at warmer times, helps to reduce exposure to the sun's rays.
In addition, wearing hats and caps are a great way to avoid sun contact with the scalp and face, regions that are more sensitive. Also important is the use of quality sunglasses, which is able to protect the eyes from UV rays.
In this way, many diseases caused by excess sun can be avoided. Find out what is the best protector for your skin and how to use it.