Most of the time, the lump in the armpit is something not worrying and easy to solve, so it's no reason to be alarmed. Some of the more common causes include the boil, inflammation of a hair follicle or sweat gland, or an enlarged lymph node, also known as anguish,
However, in some cases, it may also indicate dermatological changes, such as suprative hydrosadenitis, and only in rare cases can it indicate serious diseases, such as immunological or infectious diseases or even cancer, which is suspected only when nodules appear that grow over time or that are accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, weight loss and night sweats.
To identify the cause of a lump in the armpit, it is recommended that a dermatologist, general practitioner, or family doctor be consulted for a clinical evaluation and, if necessary, a request for tests to help determine the change.
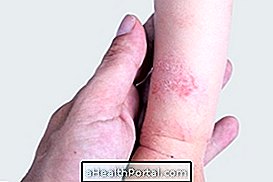
1. Folliculitis
Folliculitis is inflammation of the hair follicles, which can be due to a bacterial, fungal or viral infection of the region, or even arise when the hair is ingrown. It can cause one or several small pimples, which can be painful, reddish or yellowish due to the presence of pus, and itchy.
- What to do : After assessing the area by the doctor and observing the severity of the injury, it may indicate anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce discomfort and antibiotics to combat infection, which may be in ointment or tablet. It may also be advisable to avoid shaving the skin until it improves inflammation.
To prevent folliculitis, keep the skin clean, dry and moisturised. Check out more about what it is and how to treat folliculitis.
2. Boil
The furuncle is also caused by infection of the hair follicle, however, it is deeper and causes inflammation of the surrounding area, causing a larger, more reddish lump and producing large amount of pus.
- What to do : You should seek medical help to evaluate the area and indicate whether the boil should be drained. You can also target antibiotics in ointment or tablet, as well as warm water compresses to speed recovery.
During the treatment of the boil, and to prevent new infections, such as using antiseptic soap, wash with soap and water daily and after bursting, in addition to washing with warm water the clothes that be in contact with the region. See more about the symptoms and treatment of the boil.
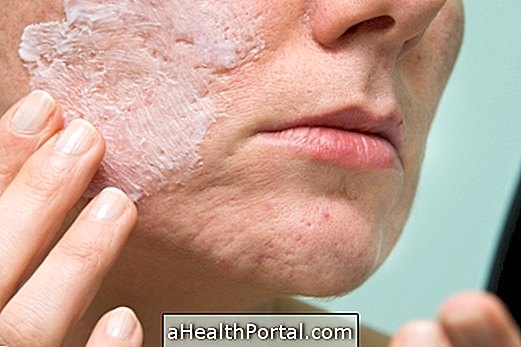
3. Hydrosadenitis suppurativa
The suppurative hydrosadenitis of the armpit is inflammation of the glands that produce sweat in this region, causing the blockage of the sweat passage out of the gland and the formation of painful lumps and leaving scars on the skin.
- What to do : A dermatologist's evaluation is needed, which will indicate treatments to decrease the symptoms of the affected region, such as antibiotic creams or corticosteroid injection in the affected region. In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected area and replace it with a graft.
Keeping the region clean, avoiding tight clothing and making wet compresses in the area can also help with treatment. Check out more about what is and how to treat suppurative hydrosadenitis.

Sebaceous cyst
The sebaceous cyst is a type of lump that arises under the skin, and which contains the accumulation of sebum, and can arise anywhere in the body. Generally, it is not painful except when it is inflamed or infected, when it can get sore, hot and red.
- What to do : The treatment is indicated by the dermatologist, and consists of making compresses of warm water and anti-inflammatory use. In some cases, minor surgery may be needed to remove the cyst.
Learn more about how to identify and treat sebaceous cyst.
5. Tongue
The tongue is the enlarged lymph node, which may arise due to any inflammation or infection of the arm, chest or breast region. This happens because the lymph node is part of the immune system, and can increase in size to produce more defense cells, to attack any germ that can bring problems to the body.
Most often, the tongue is not worrisome, and may arise from a variety of causes, such as ingrown hairs, folliculitis, furuncle, lymphadenitis, but may also indicate a systemic disease such as autoimmune disease or cancer, especially when they grow large or are located on various parts of the body.
. The main causes include:
- Inflammation or infection of hair follicles;
- Infections, such as sporotrichosis, brucellosis, cat scratch disease, lymph node tuberculosis, among others;
- Autoimmune disease, such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, dermatomyositis, or sarcoidosis, for example;
- Cancer, such as breast cancer, lymphoma, or leukemia.
Some signs that may indicate that the tongue is worrisome are growing more than 2.5 cm, have a hard consistency, adhered to the deep tissues and do not move, persist for more than 30 days, be accompanied by symptoms such as fever, weight loss or night sweats or when it appears in various places of the body.
- What to do : usually, the tongue goes away on its own after a few days or weeks of resolving the inflammation. The doctor's observation will be able to assess whether this is really an angle and whether more tests are needed to investigate the cause.
Also check out other causes of enlarged lymph nodes in the body.