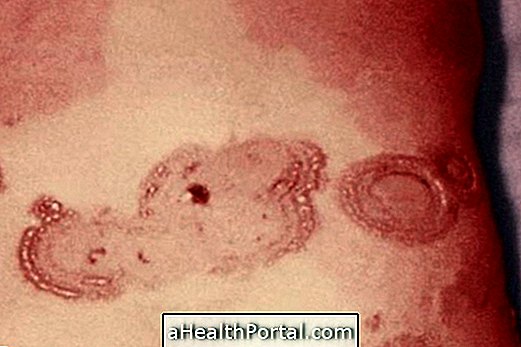
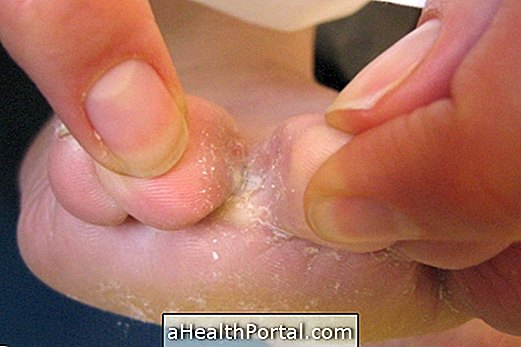
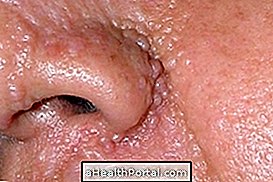
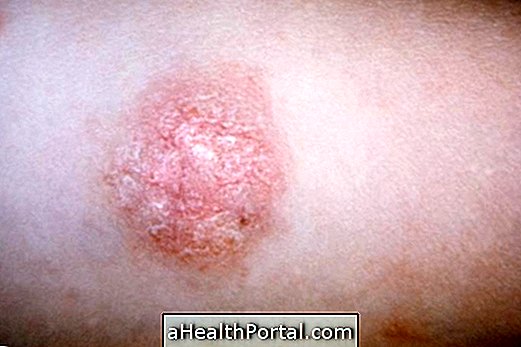
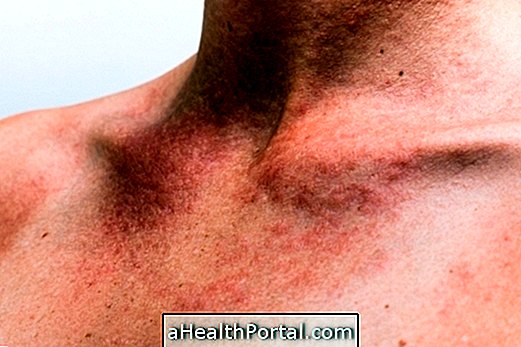
Urticaria is characterized by the appearance of spots with high relief on the skin with intense itching, which lasts about 24 hours, after which it may appear in other regions of the body.
Urticaria is an exaggerated allergic reaction, which can be triggered by several factors, such as ingestion of medications and certain foods, insects or parasites, infections, exposure to cold or heat, sun exposure, exercise and pressure on the skin. In addition, urticaria can be triggered in stressful situations, hence popularly called "nervous urticaria."
What are the symptoms
The characteristic symptoms of urticaria may be:
- Intense itching throughout the body;
- Skin irritation;
- Swelling of the epidermis;
- Appearance of redness;
- Burning in the skin.
These symptoms may appear when the person becomes anxious and stressed, however, these people are already predisposed to hives and it is only triggered or exacerbated in stress or other situations, such as exposure to extreme temperatures or contact or intake of allergens.
What is the diagnosis
The diagnosis for urticaria is a physical examination that is done by the doctor, who may also ask questions to understand what may have triggered the symptoms, such as activities that have been performed, foods or medicines ingested, areas where blemishes usually appear or frequency of onset of episodes.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment for urticaria usually involves taking antihistamines, which decrease the discomfort caused by the disease. In some cases, it may be necessary to take anti-inflammatories, monoclonal antibodies or suppressive immune system remedies. Learn more about treatment.
The symptoms usually have a negative impact on the quality of life of the person, since they can be precipitated at any time, so know how to control is important to avoid embarrassment and manifestations of the disease. Psychological counseling can be helpful.