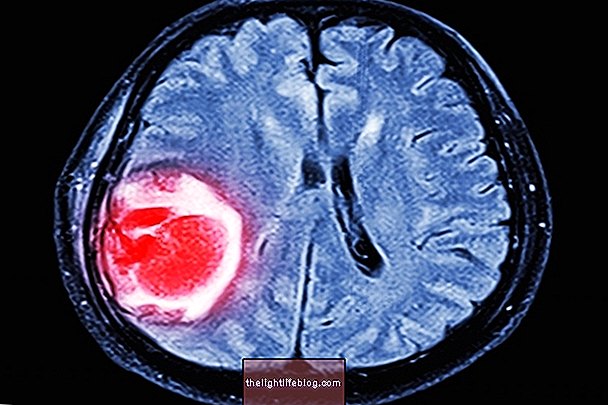
Adenocarcinoma is a type of cancer that originates in the glandular tissues, formed by cells with abilities to secrete substances for the organism. This type of malignant tumor can develop in various organs of the body, including prostate, stomach, intestine, lungs, breasts, uterus or in the pancreas, for example.
In general, adenocarcinomas are a cancer that is difficult to remove by surgery, with fast growth and aggressive character, since it has the capacity to generate metastases, however, there are specific characteristics according to each type and stage in which it is found. Some of the key examples include:
1. Adenocarcinoma of prostate
It is the cancer that arises in the glandular cells of the prostate, and is more common in men over 65 years. Although they usually grow slowly and gradually, some types can grow rapidly, aggressively and spread easily through other organs, generating metastases.
Adenocarcinoma of the prostate can also be divided into other subtypes, with acinar adenocarcinoma being the most common. Learn more about how to identify and treat prostate cancer.
2. Lung adenocarcinoma
Pulmonary adenocarcinoma is the cancer that affects the glandular cells of the lungs. It is one of the most common types of lung cancer, accounting for about 30% of cases. This type of tumor is usually aggressive, so it is important that your treatment is started as soon as possible as soon as identified. Learn more about the symptoms that indicate lung cancer and what to do to treat it.
3. Gastric adenocarcinoma
It is the malignant tumor that appears in the cells of the stomach, and represents 95% of the tumors that affect this organ, being more common in people over 50 years of age.
Symptoms that indicate this tumor include abdominal pain, weight loss, nausea and difficulty swallowing or digesting food. Check out more details about the main symptoms of stomach cancer.
4. Bowel adenocarcinoma
95% of cases of colorectal cancer are caused by adenocarcinomas, which are one of the most common cancers in the population. This type of tumor usually responds well to treatment, especially if it has been discovered early and has not reached other organs in the body, so it is very important to do the screening tests recommended by doctors, especially for people with a family history, risk factors or age greater than 50 years, such as occult blood screening or colonoscopy, for example.
Learn more about exams that can help identify bowel cancer.
5. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma
The most common type of pancreatic cancer is adenocarcinoma. They are usually aggressive tumors, because they often grow without causing symptoms and, when discovered, are in advanced stages.
Find out what are the main symptoms that can indicate and what to do in case of pancreatic tumor.
6. Breast adenocarcinoma
Breast cancer is also composed, for the most part, of adenocarcinomas. This tumor should be detected early in order to achieve better results and a greater chance of cure during treatment, so it is important to have the screening done with a gynecologist or mastologist, mammograms and self-examination.
Learn more about symptoms, treatment and how to prevent breast cancer.
Classification of adenocarcinoma
One of the ways to classify a cancer is by its type of growth, and can be:
- Adenocarcinoma in situ : it is the first stage, in which the cancer is still located in the tissue layer where they developed and there was no invasion to deeper layers and, therefore, is more easily curable;
- Invasive adenocarcinoma : arises when the cancer cells reach other layers of the tissue, can reach neighboring organs or spread through the blood or lymphatic, causing metastases;
- Well differentiated adenocarcinoma : when the cancer receives this classification indicates that they are cancer cells that still resemble the original tissue, and with slower growth;
- Low-differentiated adenocarcinoma : indicates that tumor cells have characteristics quite different from the original tissue, which may indicate greater potential for malignancy and difficulty in treatment;
- Moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma : they are at an intermediate level between good and little differentiated.
Generally, to identify the classification of cancer, it is necessary to perform a biopsy of the tumor tissue, capable of detecting these characteristics microscopically. Understand the differences between tumor and cancer and how to identify.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment for adenocarcinoma varies depending on the location, type, and classification of the tumor, but usually treatment options include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and tumor removal through surgery.
Adenocarcinomas are often aggressive and difficult to treat, so the prognosis is very individualized. However it is very important to talk to your doctor about the options, their consequences and their benefits before deciding when and where to start treatment.