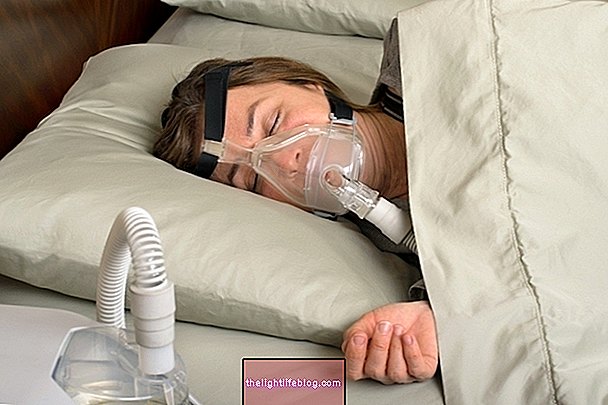
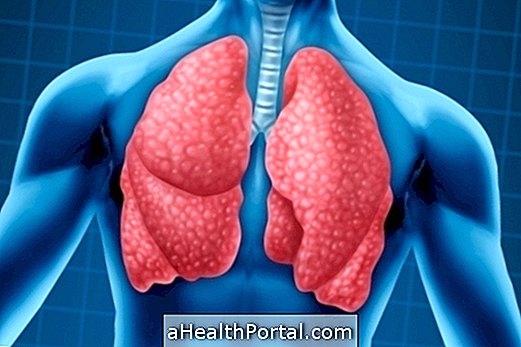
Chest pain and shortness of breath are the main symptoms of pulmonary embolism, also known as pulmonary thrombosis, a condition that occurs when a blood vessel in the lung becomes completely blocked and does not allow blood to flow properly.
Thus, to identify a case of pulmonary thrombosis, one should be aware of symptoms such as:
- Sudden sensation of shortness of breath;
- Chest pain that worsens on deep breathing, coughing or eating;
- Constant cough;
- Swelling of the legs or pain when moving the legs;
- Pale, cold, bluish skin;
- Low fever;
- Excess sweat production;
- Fast, irregular heartbeat;
- Dizziness that does not improve.
If you have more than one of these symptoms it is advisable to go to the emergency room or immediately call an ambulance to confirm the diagnosis and receive the appropriate treatment, which if not done quickly, can lead to death.
How to confirm the diagnosis
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism may be confused with a heart problem, so your doctor usually uses diagnostic tests such as a blood test, chest X-ray, CT scan, or pulmonary angiogram to confirm your suspicions and start treatment.
Who is most at risk
Although pulmonary thrombosis can occur in anyone, it is more common in cases of:
- History of heart disease or cancer;
- Prolonged immobilization, such as after surgery or during a very long plane ride;
- Overweight;
- Supplementation with estrogens.
In addition, poor lifestyle habits, such as cigarette smoking, overeating or overeating, may also increase your chances of suffering from pulmonary embolism.
Here are some tips to avoid complications such as thrombosis.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment for pulmonary embolism includes administering oxygen to the subject through a mask, plunger medications such as heparin, which will dissolve the clot that is blocking the passage of blood, and analgesics to relieve pain.
Usually, treatment for pulmonary embolism requires hospitalization that can last for a few weeks or months. Surgery for removal of the thrombus may be indicated in the most severe cases or when obstruction of blood flow occurs due to a foreign object or piece of bone, for example.
Check out more about how pulmonary embolism is treated.