Aspergillosis is a disease caused by the fungus Aspergillus furmigatus, a type of mold that can develop inside the home, but also outdoors, and is therefore very easy to get in touch with. However, most people do not develop the disease, since the immune system can eliminate the fungus.
Thus, this type of infection is more frequent in people with weakened immune systems, as in cases of asthma, HIV, lupus or after a transplant, for example.
Although the infection usually starts in the lungs, with symptoms such as coughing, shortness of breath and fever, it can quickly worsen, affecting other parts of the body such as the brain, heart or kidneys, especially when oral antifungal treatment is not started.

Main symptoms
The symptoms of aspergillosis vary according to the affected site and the severity of the infection, however the most common cases are:
1. Allergic reaction
It occurs mainly in people with a history of chronic lung diseases such as asthma or cystic fibrosis and includes signs such as:
- Fever above 38ºC;
- Coughing up blood or phlegm;
- Feeling of shortness of breath;
- Coriza and difficulty to smell.
This is the least serious type of reaction, and in most cases it can even be treated with medicines that were already being used for asthma attacks, for example. However, if the symptoms are getting worse it is very important to go to the hospital.
2. Pulmonary aspergillosis
These cases are also very common, but usually affect people who have no history of lung disease. Symptoms include:
- Weight loss;
- Persistent cough;
- Coughing up blood;
- Excessive tiredness;
- Sensation of shortness of breath.
If not properly treated, the lung infection can develop and spread through the blood, reaching into other parts of the body.
3. Invasive aspergillosis
It is the most serious type of infection that occurs when the fungus can multiply in the lungs and then spread through the blood. Signs of this type of aspergillosis can be:
- Fever above 38º C;
- Chest pain;
- Persistent cough;
- Joint pain;
- Headache;
- Swelling of the face.
Invasive aspergillosis is the most frequent type when the immune system is very weakened and therefore its symptoms can be difficult to identify, since they can be interpreted as symptoms of the disease that this in the base of the decrease of the defenses of the organism.
How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis of aspergillosis can be made by culturing the infected tissue, observing the sputum through the microscope or by examining blood with serology that detects specific antibodies against this fungus.
What treatment?
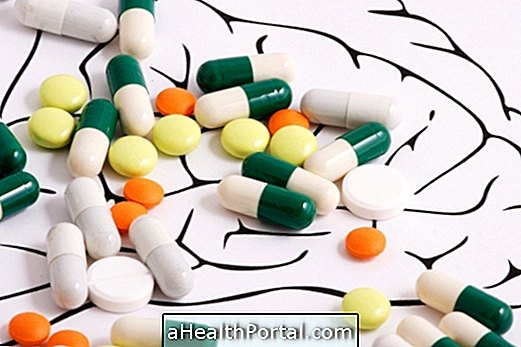
Treatment for aspergillosis is usually started with the ingestion of antifungal medicines such as Itraconazole or Amphotericin B, which helps to eliminate excess fungi from the body, helping the immune system control infection and relieve symptoms.
However, your doctor may also advise you to use corticosteroids, such as Budesonide or Prednisone, to relieve symptoms more quickly and improve the antifungal effect, especially in people with very severe symptoms, such as those with asthma.
In the more severe cases of invasive aspergillosis, in which a mass of fungi can develop, the doctor may undergo surgery to remove the most affected tissues and facilitate the antifungal effect.